-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
Securing CentOS with iptables
Read this article to get a better understanding on how to secure your CentOS with iptables.
The Cloud Raya instance control panel has its own security firewall which based on ports (TCP, UDP, and ICMP), you can manage it through the customer panel or URL https://cp.cloudraya.com/
However. In this article, we would give you the next layer for Hardening Server Security using iptables on the OS level, specifically CentOS. Securing Linux server is important to protect your data, intellectual property, from the hands of crackers (hackers) or even DDoS (Denial-of-service attack).
This Linux based firewall is controlled by the program called iptables to handles filtering for IPv4.
Prerequisites
Before we begin to the tutorial, the following are the software stack versions in this article:
- OS: Centos 7
- IPTables: v1.4.21 (Installed already by default)
- IPv4 network
Manage IPTables Firewall rule
By default, IPTables is running and no rules, you can check it by executing the following command:
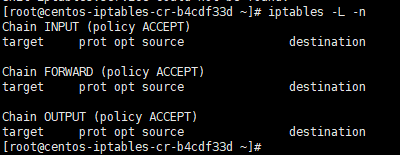
iptables -L -n
it will show you the following output:
[root@centos-iptables-cr-b4cdf33d ~]# iptables -L -n Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
The following are we mentioned some iptables which based on rules can filter high degree of illegitimate access.
# Modify this file accordingly for your specific requirement. # 1. Delete all existing rules iptables -F # 2. Set default chain policies iptables -P INPUT DROP iptables -P FORWARD DROP iptables -P OUTPUT DROP # 3. Block a specific ip-address #BLOCK_THIS_IP="x.x.x.x" iptables -A INPUT -s "$BLOCK_THIS_IP" -j DROP # 4. Allow ALL incoming SSH iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 22 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 5. Allow incoming SSH only from a sepcific network iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -s 192.168.200.0/24 --dport 22 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 22 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 6. Allow incoming HTTP iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 80 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # Allow incoming HTTPS iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT #iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 443 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 7. MultiPorts (Allow incoming SSH, HTTP, and HTTPS) iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80,443 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp -m multiport --sports 22,80,443 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 8. Allow outgoing SSH iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --dport 22 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --sport 22 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 9. Allow outgoing SSH only to a specific network iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp -d 192.168.101.0/24 --dport 22 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --sport 22 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 10. Allow outgoing HTTPS iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --dport 443 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --sport 443 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 12. Ping from inside to outside iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-reply -j ACCEPT # 13. Ping from outside to inside iptables -A INPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp --icmp-type echo-reply -j ACCEPT # 14. Allow loopback access iptables -A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o lo -j ACCEPT # 15. Allow packets from internal network to reach external network. # if eth1 is connected to external network (internet) # if eth0 is connected to internal network (192.168.1.x) iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o eth1 -j ACCEPT # 16. Allow outbound DNS #iptables -A OUTPUT -p udp -o eth0 --dport 53 -j ACCEPT #iptables -A INPUT -p udp -i eth0 --sport 53 -j ACCEPT # 18. Allow rsync from a specific network iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -s 192.168.101.0/24 --dport 873 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 873 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 19. Allow MySQL connection only from a specific network iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp -s 192.168.200.0/24 --dport 3306 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 3306 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 20. Allow Sendmail or Postfix iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 25 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 25 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 21. Allow IMAP and IMAPS iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 143 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 143 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 993 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 993 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 22. Allow POP3 and POP3S iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 110 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 110 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i eth0 -p tcp --dport 995 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -p tcp --sport 995 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT # 23. Prevent DoS attack iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m limit --limit 25/minute --limit-burst 100 -j ACCEPT # 24. Port forwarding 80 to 8080 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 8080 # 25. Log dropped packets iptables -N LOGGING iptables -A INPUT -j LOGGING iptables -A LOGGING -m limit --limit 2/min -j LOG --log-prefix "IPTables Packet Dropped: " --log-level 7 iptables -A LOGGING -j DROP
Manage IPTables Firewall rule (continue)
Furthermore, We can then add a few simple firewall rules to block the most common attacks, to protect our instance in Cloudraya from script-kiddies. We can’t really count on iptables alone to protect our instances from a full-scale DDOS or similar, but we can at least put off the usual network scanning bots that will eventually find our instances and start looking for security holes to exploit.
First of all, we start with blocking null packets.
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL NONE -j DROP

We told the firewall to take all incoming packets with TCP flags NONE and just DROP them all. Null packets are simply said recon packets. The attack patterns use these to try and see how we configured the Instances and find out weaknesses.
Fragmented Packet:
iptables -A INPUT -f -j DROP

All packets with incoming fragments drop them. This attack result in Linux server panic such data loss.
Force SYN Packet Check:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp ! --syn -m state --state NEW -j DROP

Ensure all NEW incoming TCP connections are SYN packets. Otherwise, we need to drop them, SYN-Flood-Attacks means that the attackers open a new connection, but does not state what they want (ie. SYN, ACK, whatever). They just want to take up our servers’ resources. We won’t accept such packages.
XMAS Packet:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --tcp-flags ALL ALL -j DROP

All incoming malformed XMAS packets should be dropped, XMAS packets is also a recon packet.
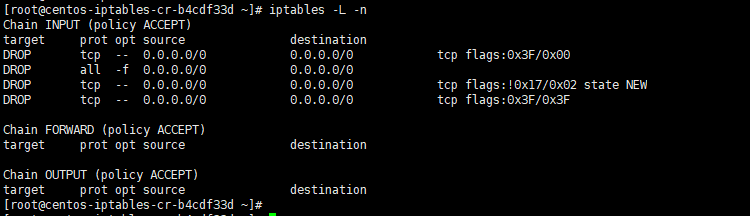
The following are all rules above that we have added (blocking null packets, Fragmented Packet, Force SYN Packet Check and XMAS Packet).
[root@centos-iptables-cr-b4cdf33d ~]# iptables -L -n Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination DROP tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp flags:0x3F/0x00 DROP all -f 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 DROP tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp flags:!0x17/0x02 state NEW DROP tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp flags:0x3F/0x3F Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT) target prot opt source destination
We also recommend you to install and use sniffer such as tcpdump and ngrep to test your firewall settings
Conclusion
This article only lists basic rules for new Linux users. You can create/custom and build more complex rules. This requires a good understanding of TCP/IP, Linux kernel tuning via sysctl.conf, and good knowledge of your own setup.
Hope this helps and see you in the next article.