-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
When you have a private cloud or public cloud infrastructure, you won’t need public IP on every server or service you have. It is unnecessary and costly to have many public IPs assigned to your infrastructure. However, you will also need a way to access and manage your cloud servers securely. This is where VPN comes in
VPN or Virtual Private Network is a way to connect to your infrastructure securely. With many ways to set it up, from a complicated custom one that attaches to your physical firewall, to a simple VPN application deployed on your Virtual machine.
In Cloudraya, you can actually deploy VPN easily. You just need to go to the Dashboard and follow this tutorial to set up your own VPN connection to Cloudraya
Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
So What’s the Deal?
However, due to its nature, Cloudraya VPN has virtually supported Windows and Linux clients.
This is due to its setup, a client that wants to connect to Cloudraya VPN needs to be set with MS-CHAPv2 which is not supported by newer MacOS clients.
If you having trouble connecting to Cloudraya VPN, or in need of a more advanced function of VPN setup, this tutorial is good for you.
In this tutorial, you will set a VPN virtual machine, which includes a DNS-Level Adblocker. So, clients that connect to this VPN will also get an ad-free browsing benefit.
Preparing the Virtual Machine
You can use any Virtual Machine in any Cloud Provider. However, if you deploy in Cloudraya, you will need a x-small Ubuntu 20.04 package and deploy the virtual machine.
For further details of creating a new VM, you can refer to this article: Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya – Cloudraya KB
You will also need to open the following port and protocol on Cloudraya Security Profile:
- Port 51820/tcp
- Port 51820/udp
- Port 51821/tcp
- Port 80/tcp
You can refer to this article on how to add rules on Cloudraya Security Profile: Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile – Cloudraya KB
PiHole DNS Server Installation
PiHole is a DNS server that includes an Adblocker as its feature. Thus, when you connect to this DNS server, PiHole will process your query and will decide whether the domain name is blocked or allowed to access.
We will not make this VM DNS Server public since it will create whole another great mess, so we will only allow the DNS server to be served to any client connected to the VPN.
To install PiHole, run this command under root user:
curl -sSL https://install.pi-hole.net | bashUpon installation, you will get this message
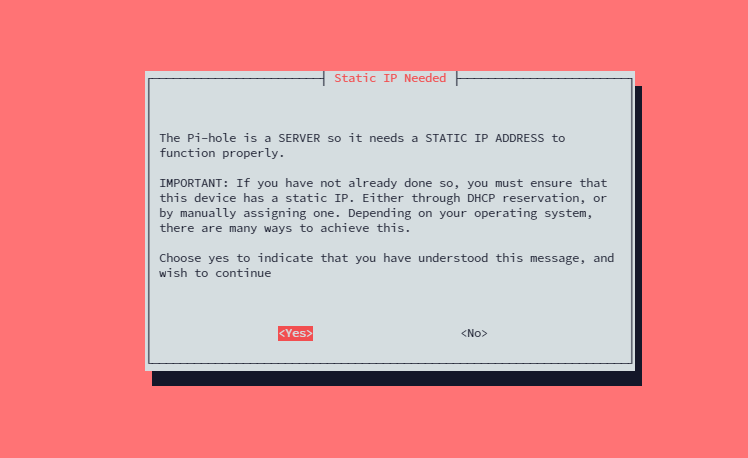
Click Yes, since the VM is already having proper Public and Private static IP.
On the next page, you must select the upstream public DNS server that this VM will connect to. You can select Google (ECS, DNSSEC) or Cloudflare (DNSSEC) for the most stable upstream.
Then, click on yes if you are asked to “install web admin interface”. So you can easily manage the PiHole. Also, click on ON to “install lighttpd”
After that, click on yes until installation starts.
At the end of the installation, you will get useful installation information such as below:
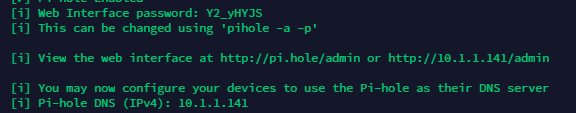
Change the password to make the web interface more secure.
That’s it for the PiHole installation, we are now halfway to setup our VPN Server. Continue with the PiVPN installation
PiVPN Installation
PiVPN is a simple setup VPN application that uses WireGuard or OpenVPN as its backend. WireGuard or OpenVPN is a robust and reliable VPN protocol that is used worldwide.
To deploy PiVPN, run this command as root user
curl -L https://install.pivpn.io | bashThis command will automatically start the PiVPN installation.
On installation progress, you will be asked a few questions
First, you will be asked a non-root user that will hold a VPN configuration. If you have no users, the installer will create them for you
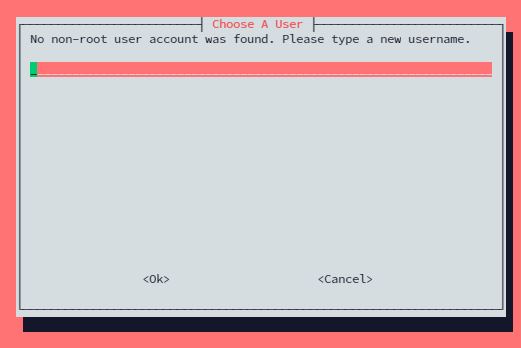
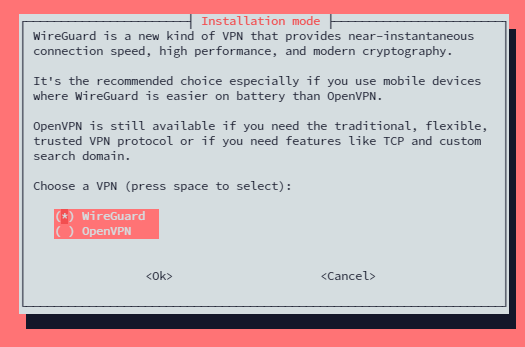
After you create a new non-root user, you will be asked whether you will use WireGuard or OpenVPN.
You should use WireGuard since it has a simpler client experience on Windows, Ubuntu and macOS, even on Android.
When asked what port you should use, use the default port (51820). This is the port that we have opened on Cloudraya Security Profile earlier.
After that, you will be asked by the installer to use PiHole as its DNS, click on Yes
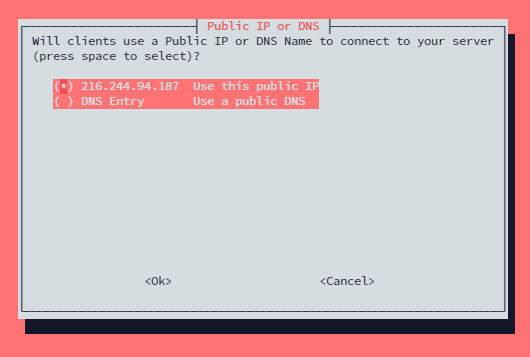
Since this server only has a Public IP, select the IP when asked the below question. Also, it is recommended to select IP for a more stable experience.
When the below information is shown, that means the installation has succeeded.
You can now use the VPN server and add users using the Terminal.
However, why stop there? We also can set up PiVPN dashboard, so we can easily add or remove VPN users.
Install PiVPN Dashboard
To install PiVPN-Web Dashboard, we will need to install docker on our VPN server.
This container is not taking high resources and is easily deployable and manageable.
To set up Docker, run the below command:
# Install Docker
curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh
sudo sh get-docker.sh
# Add user 'pi' to group 'docker'
sudo usermod -aG docker pivpnAfter docker is installed successfully, run this command to install PiVPN-Web
docker run -d -p 51821:51821 --name pivpn-web --restart=unless-stopped weejewel/pivpn-webThat’s it, now your VPN Server is up and running. Now we will continue to set up a new user and client on Ubuntu, Windows, and macOS
Modify User on PiVPN-Web Dashboard
First, navigate to this address on your web browser:
http://<your public ip>:51821/Then, log in to your root user account.
After authenticated you will be greeted with this screen
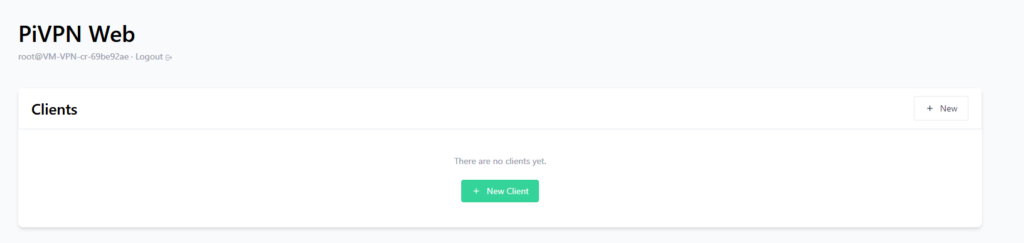
Click on New Client and type a new name for this VPN client.
After you created a new client, you will have your new user with an option on the right side
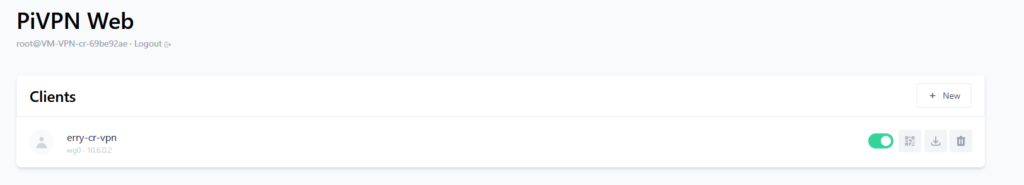
The option from the rightmost side is:
- Delete Profile (Trash bin icon) : Delete this profile
- Download configuration : Download configuration to add them on the VPN client
- Show QR Code : If you connect to mobile device, you can easily add the configuration by taking the QR Code of the configuration
- Profile Enable Toggle : Enable or Disable account without deleting the profile.
Now, we will set the VPN client, so they able to connect to the VPN server
Configure VPN Client on Windows
To be able to connect with the VPN server, you need to download WireGuard application.
In Windows, there is an application called WireGuard for Windows you can download the application on the link below:
Download Windows Installer (wireguard.com)
Open the Installer and complete the installation. After that, open the application.
First, download the configuration on PiVPN Web. Then click on Add Tunnel. Navigate to your file and download
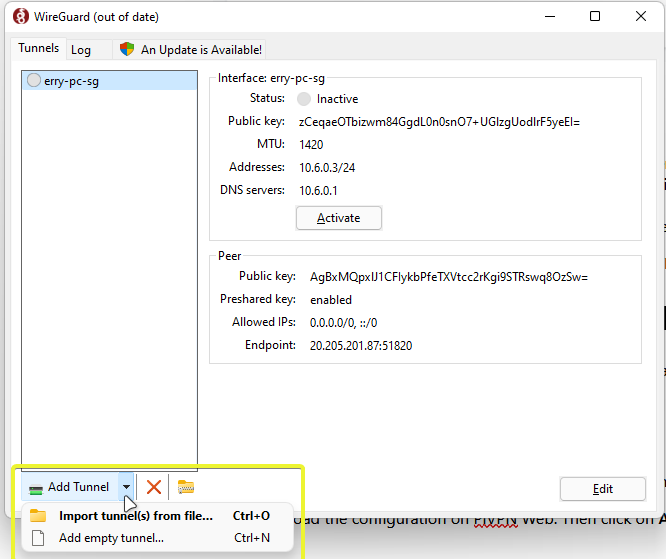
Then click on Activate.
Configure VPN Client on Ubuntu
Since there is no GUI Client on Ubuntu, we need to add features into Ubuntu Network Manager. This method is confirmed working on Ubuntu 20.04
First, you need to run this command to install the to build the features
sudo apt install wireguard git dh-autoreconf libglib2.0-dev intltool build-essential libgtk-3-dev libnma-dev libsecret-1-dev network-manager-dev resolvconfAfter the installation for the above package is completed, run the below command to compile and add a feature in Ubuntu Network Manager
git clone https://github.com/max-moser/network-manager-wireguard
cd network-manager-wireguard
./autogen.sh --without-libnm-glib
./configure --without-libnm-glib --prefix=/usr --sysconfdir=/etc --libdir=/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu --libexecdir=/usr/lib/NetworkManager --localstatedir=/var
make
sudo make installIf the installation is successful, when you open Ubuntu Network Manager, and click on add VPN you will see WireGuard and Import from file this means that you are ready to add Wireguard profile
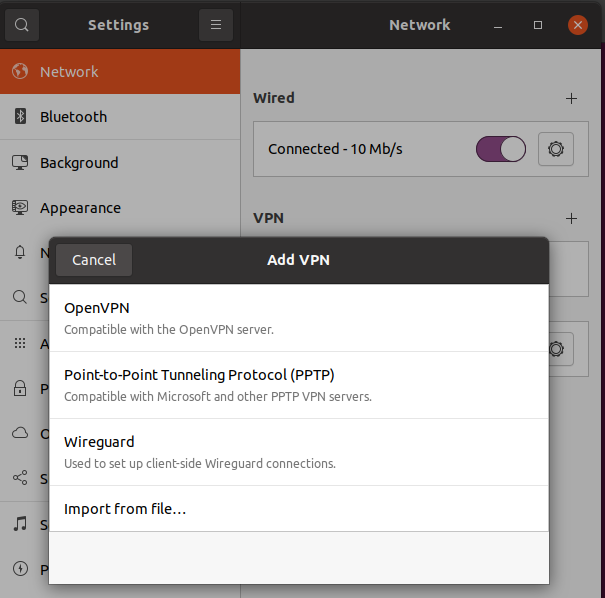
Select Import from file then adds your profile.
After that, you are able to connect to your VPN server correctly.
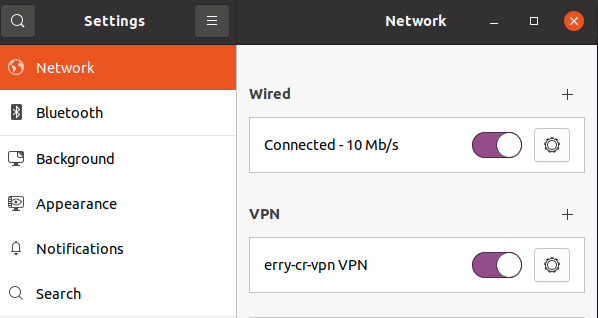
Configure VPN Client on MacOS
There is also a WireGuard Client on Mac AppStore. You can download it here.
WireGuard on the Mac App Store (apple.com)
After you successfully install it from Mac App Store, open the application. Then click on the + icon on the bottom-left of the window and click on Import Tunnel(s) from File. then select the configuration file
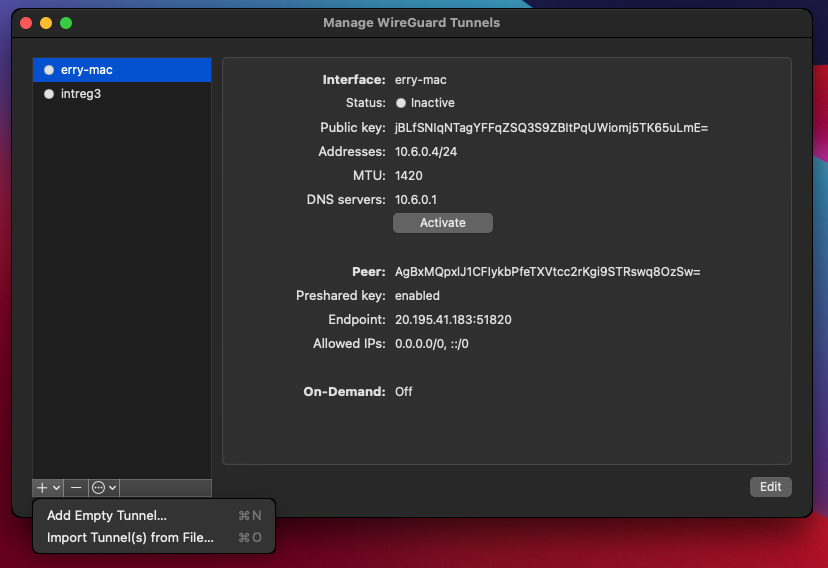
After it has been successfully added, click on Activate.
You are now able to connect to your VPN Server
Configure VPN Client on Android
There is an available GUI client on Android. Open Play Store and download Wireguard
After that, open the Wireguard application and click on the Blue (+) button
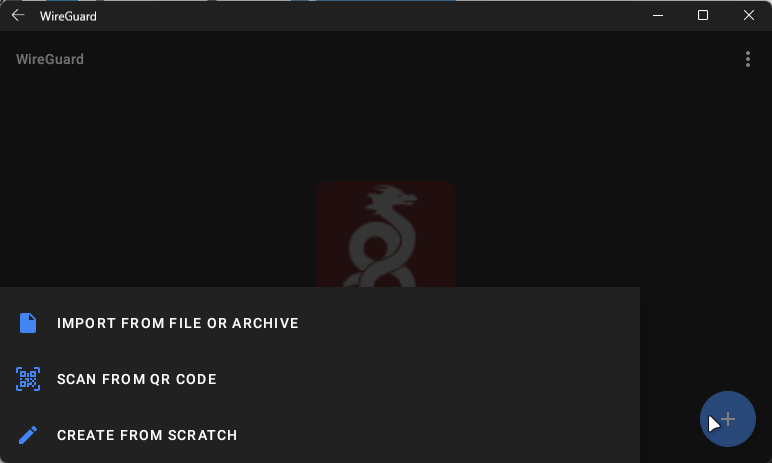
You can pick a way to add the profile. Import from file or archive is the same way as the other OSes, you can use the configuration file. Or you can scan from QR code.
To get the QR code for your profile, navigate to PiVPN-Web Dashboard and click on the Show QR Code on the right side of the profile

After that, a QR Code will appear, scan it using your android phone.
Just like that, the profile will appear on your application. Now you can connect to your VPN server using android
Closing
Wireguard is a lightweight and robust VPN server application that also have a multiplatform client. It can be deployed easily using PiVPN script and managed using PiVPN-Web. It also can be equipped with PiHole, a DNS Level Adblocker. Using those tools, you can create a VPN server fast, easy and secure.
Reference:
Pi-hole – Network-wide protection
GitHub – WeeJeWel/pivpn-web: 🚀 Web UI for PiVPN
PIVPN: Simplest way to setup a VPN