-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
Introduction
In this article we will show you how to deploy Magento on Cloud Raya. Before we begin, let’s get to know about the Magento.
In short, Magento is a content management system focus on eCommerce, that helps the users to create eCommerce websites. It was released on March 31, 2008, by Varien, and then developed on Zend Framework.
In addition, there are some basic features of Magento:
- Product management: able to manage product such as product images, product reviews, favourite product list, and product list.
- Category management: to help user find and then select products by category easier.
- Inventory management: it shows management of products quantity and also the options.
- Client account: It shows account status, transaction history, preferred catalog, address, and also shopping cart.
- Customer service: allows the admin to assist the customer actions, such as cancel order, order tracking and history from account, reset mail and password, etc.
- Order Management: this feature relates to order as well as invoice management. So, the admin able to view, edit, create, and fulfill orders and/or invoices from the admin panel.
- Payments: many payment methods such as credit card, PayPal, Google Checkout, support for external payment modules like CyberSource, ePay, eWAY, and more.
- Search technology: it is fast, friendly, and also support search on Google SiteMap.
- International support: Language support, multiple currencies, as well as tax rates.
- Promotion and marketing tools: it includes coupons, promotions, and many more.
- Analyze and report: it integrates with the Google Analytics service and also provide multiple reports.
Installation Stage
1. System Requirements and Package Installation
In this article, we will deploy Magento in a single node environment. While, the Magento deployment in the cluster may need addition environment and steps. The requirements for a single node deployment are described as below:
- Virtual Server with Ubuntu 20.04 x86_64 and 4 GB minimum memory
- Nginx 1.x, as a web server
- PHP7.4-FPM, and the extensions needed
- MariaDB 10.4 as a database
- Elasticsearch 7.x, as an indexing engine (required by Magento)
- Composer 1.10.16
1.1 Creating a virtual machine in Cloud Raya
Please find the virtual machine creation steps on this link. After that, Select Ubuntu 20.04 as a based OS in the image selection, and choose a package with a minimum 4 GB memory resource.
1.2 Installing Nginx 1.x Web Server
- First of all, please update the current Ubuntu repository by running this command $ sudo apt update.
- Then, Install the Nginx package from Ubuntu repository $ sudo apt install nginx -y.
- Next, check the nginx version by executing $ nginx -v
1.3 Installing PHP7.4-FPM and the required extensions
- Firstly, type this command to install PHP7.4-FPM in the virtual machine $ sudo apt install php7.04-fpm -y
- After that, Verify the PHP version
$ php -v - Then, add the required php extentions to the system.
$ sudo apt install -y php74u-pdo php74u-mysqlnd php74u-opcache php74u-xml php74u-gd php74u-devel php74u-mysql php74u-intl php74u-mbstring php74u-bcmath php74u-json php74u-iconv php74u-soap1.4 Installing MariaDB 10.4
- First, setup the repository and install it to the virtual machine by following this link.
- We can also follow the secure installing process in the link above to hardened our MariaDB
- Run the following command to install the dependency of MariaDB 10.4
$ sudo apt install -y mariadb-server-10.04 mariadb-client-10.4 - Then, login the to the MariaDB server to determined its version
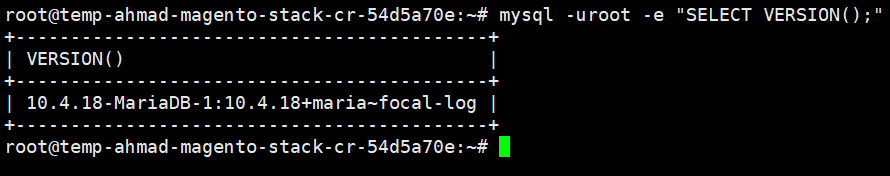
1.5 Installing Elasticsearch 7.x
- We need Java Development Kid (JDK) before adding Elasticsearch into the virtual machine. We can install the JDK using the following command
$ sudo apt install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk - Follow this link for Ubuntu or Debian based platform.
- Please also make sure the Elasticsearch service is running after it’s started.
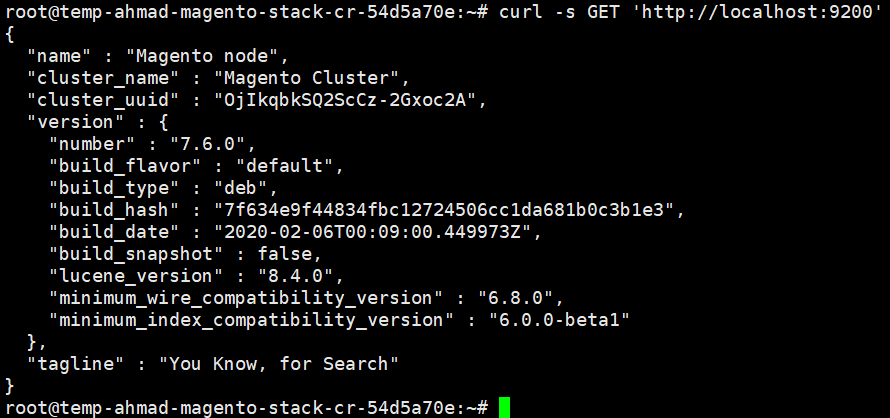
1.6 Installing Composer
- Composer’s manual suggests to not run the command using a root or super privileged. So, we will create a temporal user to execute the composer command.
- Create a temporal user using the command below, and add it to www-data usergroup
$ sudo adduser admuser$ sudo usermod -aG www-data admuser- Then, download the composer file direct from the internet. Then move the file to /usr/local/bin directory
$ sudo curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php
$ sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer- Run the following command to change the composer version to 1.10.16
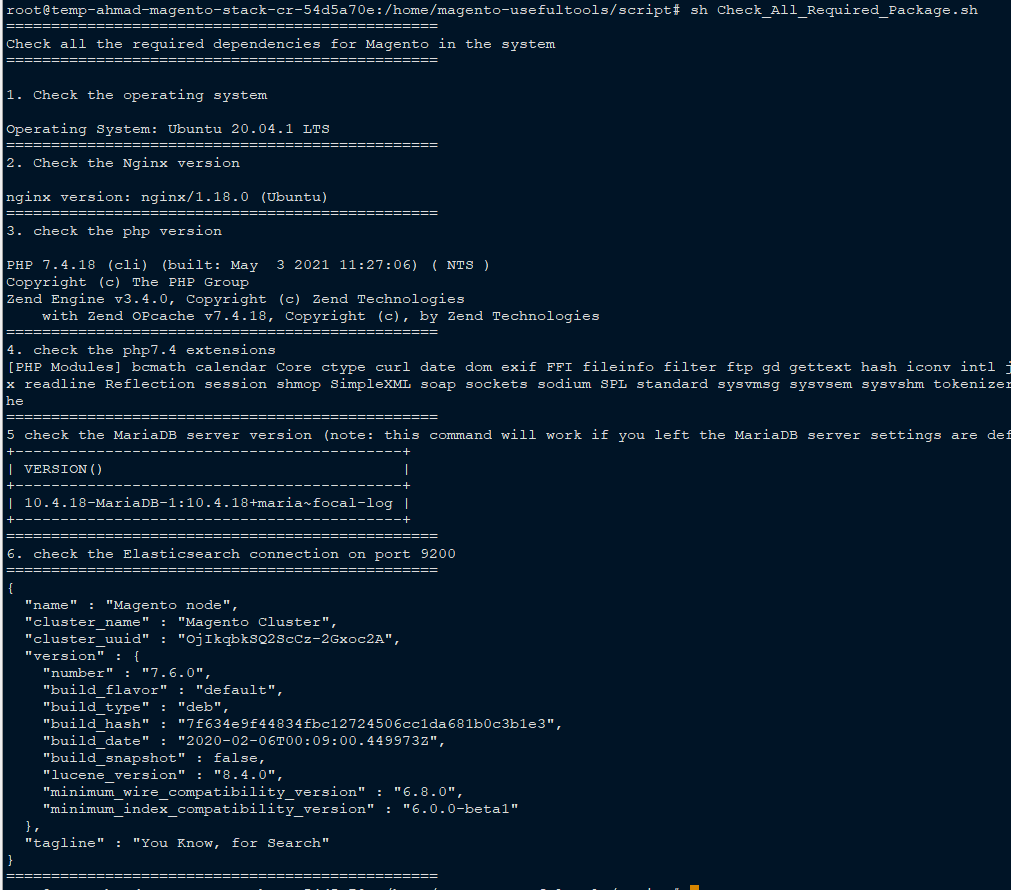
$ composer self-update 1.10.16Let’s check the all the installed dependencies using the simple script below
$ git clone https://github.com/kingahmadr/magento-usefultools.git; cd magento-usefultools/script$ sh Check_All_Required_Package.sh
Minimal Configuration
In this section, We will tweak the configuration of all Magento dependencies on the virtual machine with a minimal tweaking.
2. Configuring Nginx and Terminate SSL
We will configure the Nginx web server, to use the PHP-FPM as an upstream connection and configure the SSL Certificate on the domain.
- Create the domain file configuration in directory /etc/nginx/sites-available
$ sudo touch <name of your domain>.<tld>
2.1 Domain Configuration
- Configure the domain in /etc/nginx/sites-available as the following example:

- Line 1 – 5 describes a fastcgi backend server between Nginx web server and PHP-FPM.
- 6 – 12, is a function to redirect http connection of the domain to an https connection.
- 15 – 17, described the name of the domain listened, and set the MAGE_ROOT variable to /var/www/magento (the Document Root of our Magento Platform).
NOTE The server_name value in the configuration is a domain name that you have bought from the registrar
- 19, describes an included Nginx configuration in directory /var/www/magento. Magento provides a template configuration of nginx web server on their directory. We can included that configuration in our nginx configuration.
- 21 – 24, define the SSL certificate file and SSL certificate key file directory. In this lines, it will be used by the web server to perform an SSL termination.
- 27 – 34, the directives for SSL hardening purposes.
Create a symbolic link to /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/ahmadcloud,life.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ahmadcloud.life.conf
Test the Nginx configuration by execute nginx -t command. If the test success, execute the “nginx -s reload” to reload the current configuration
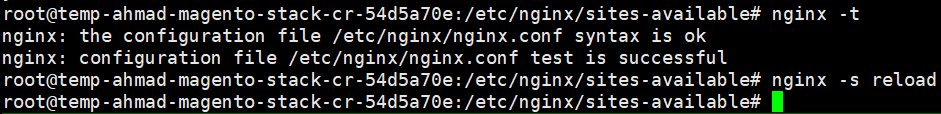
2.2 Configuring PHP
Find the php configuration file in /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php.ini & /etc/php/7.4/cli/php.ini. Don’t forget to backup the original configuration of php.ini
- Firstly, set the system time zone for PHP. Locate the following setting and uncomment it if necessary
date.timezone =
- Then, increase the values for the PHP
realpath_cache_size, andrealpath_cache_ttlto recommended settings.
realpath_cache_size=10M
realpath_cache_ttl=7200- Enable opcache.save_comments, which is required for Magento 2.1 and later. Locate the opcache.save_comments directive and uncomment it if necessary. Make sure its value is set to 1
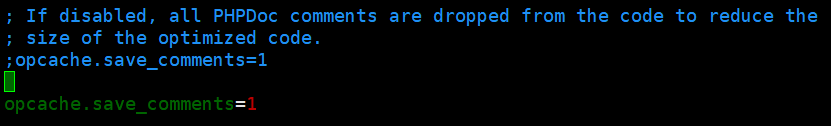
- Next, change the value of memory_limit, max_execution_time and zlib.output_compression to one of the values recommended.
memory_limit = 2G
max_execution_time = 1800
zlib.output_compression = On
2.3 MariaDB instance Configuration
In this section we will discuss how to create a new database instance for Magento. Although we recommend a new database instance, you can install Magento into an existing database instance (optionally).
- before that, login to your database server using a privileged user
$ mysql -uroot
- Enter the following commands in the order shown to create a database instance named magento with username magento:
creating a new databasecreate database magento;make a new user with a localhost access
create user 'magento'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'R2phuYzuMAEG8jgS';Grant all privilege to user magento@localhost to database magento
GRANT ALL ON magento.* TO 'magento'@'localhost';flush privileges; - Verify the database
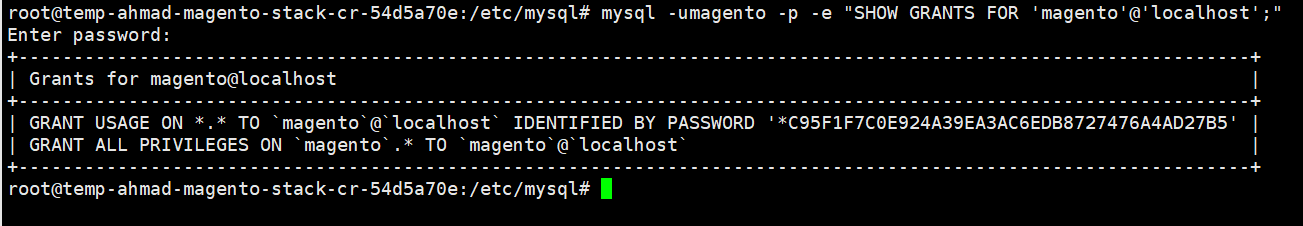
2.3.1 Magento Database Tweaking
We recommend you to configure your database instance as appropriate for your business. When configure your database, please keep the following in mind:
- Indexers require higher tmp_table_size and max_heap_table_size values (e.g., 64M). If you configure the batch_size parameter, you can adjust that value along with the table size settings to improve indexer performance.
- For optimal performance, make sure all MySQL and Magento index tables can be kept in memory (e.g., configure innodb_buffer_pool_size)
- Reindex process on MariaDB 10.4 takes more time compared to other MariaDB or MySQL versions. To speed up reindex process, we recommend setting these MariaDB configuration parameters,
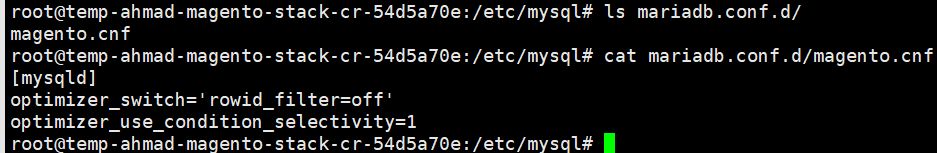
optimizer_switch=’rowid_filter=off’, optimizer_use_condition_selectivity = 1
To set those variable permanently, We will create the *.cnf file in /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/ directory. We will name the file as magento.cnf
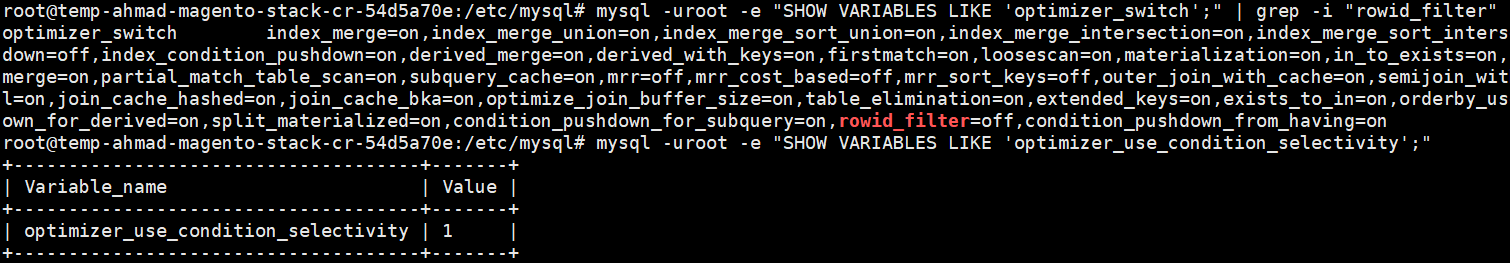
To check the variable’s value, we can execute the below command:
mysql -uroot -e "SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'optimizer_switch';" | grep -i "rowid_filter" \
&& mysql -uroot -e "SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'optimizer_use_condition_selectivity';"
2.4 Elasticsearch Configuration
There are three things we would like to change in the file configuration (/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml)
- Update the Cluster Name by replacing the cluster.name value, with something descriptive, for instance “Magento Cluster”.
- Then, update the Node Name, replace the node-name value with something descriptive like “Magento Node”
- You need to update the Network Host also. And finally do the same with network.host , replacing the IP (“192.168.0.1”) with “localhost”.
- Lastly, Save the configuration and restart the service.
# systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
3. Deploy Magento using composer
First of all, we will need a Magento Marketplace account and generate a set of keys during the Magento 2.4 installing process. Once sign into Magento Marketplace, navigate to My Profile. Under the Marketplace tab, click on Access Keys. After that, under the Magento 2 tab click the Create A New Access Key button. In the Popup, give this an proper name such as the Business Name of the website you plan to install (note, you cannot use spaces). Once you generate your Public Key and Private Key, put them somewhere safe for later.
- To begin the Magento installation using composer, first navigate to Magento Document Root (/var/www/magento)
- Change the folder owner to admuser:www-data
# cd /var/www
# chown -R admuser:www-data magento
# cd magento
- Execute the composer installer as an admuser user
# su admuser -c “composer create-project –repository-url=https://repo.magento.com/ magento/project-community-edition=2.4.0 .”
- During the setup, we will be asked for a Username and a Password. Just to be clear, Username = Public Key and Password = Private Key. Once underway, the composer process can take anywhere from 5-10 minutes to complete
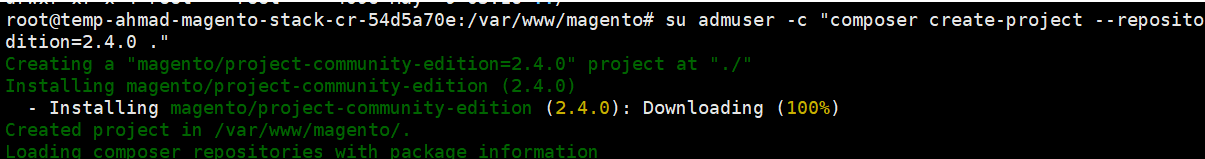
- In the current directory run the following instruction to setup Magento with a described environment. You must define your own to fullfill your needs. Below are just an example of my setup.

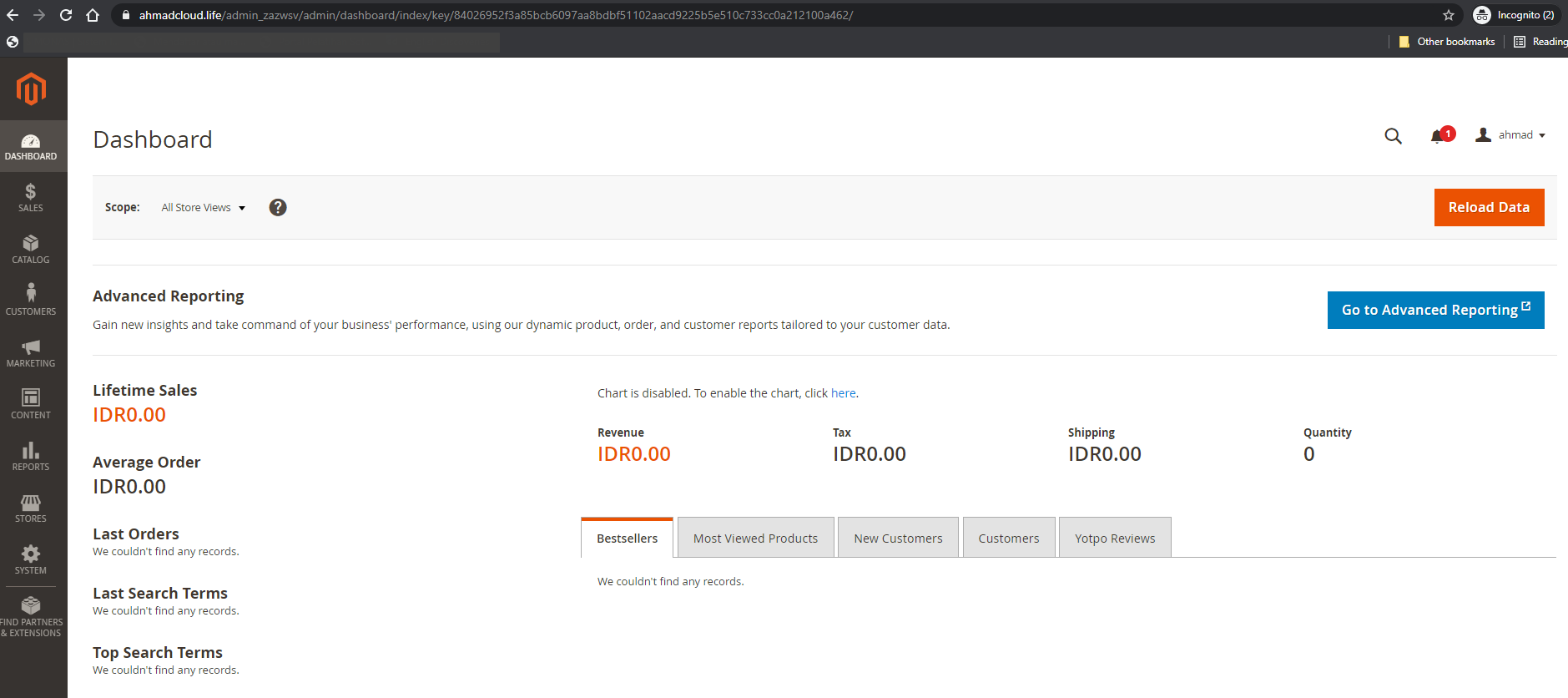
Once the setup is complete, it will look like this
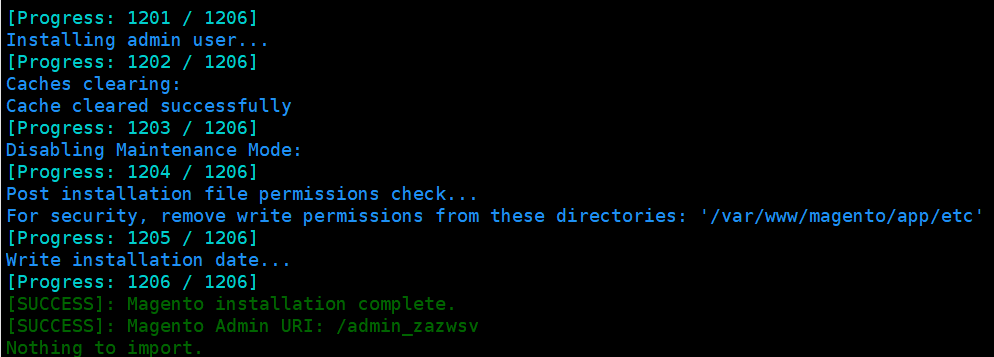
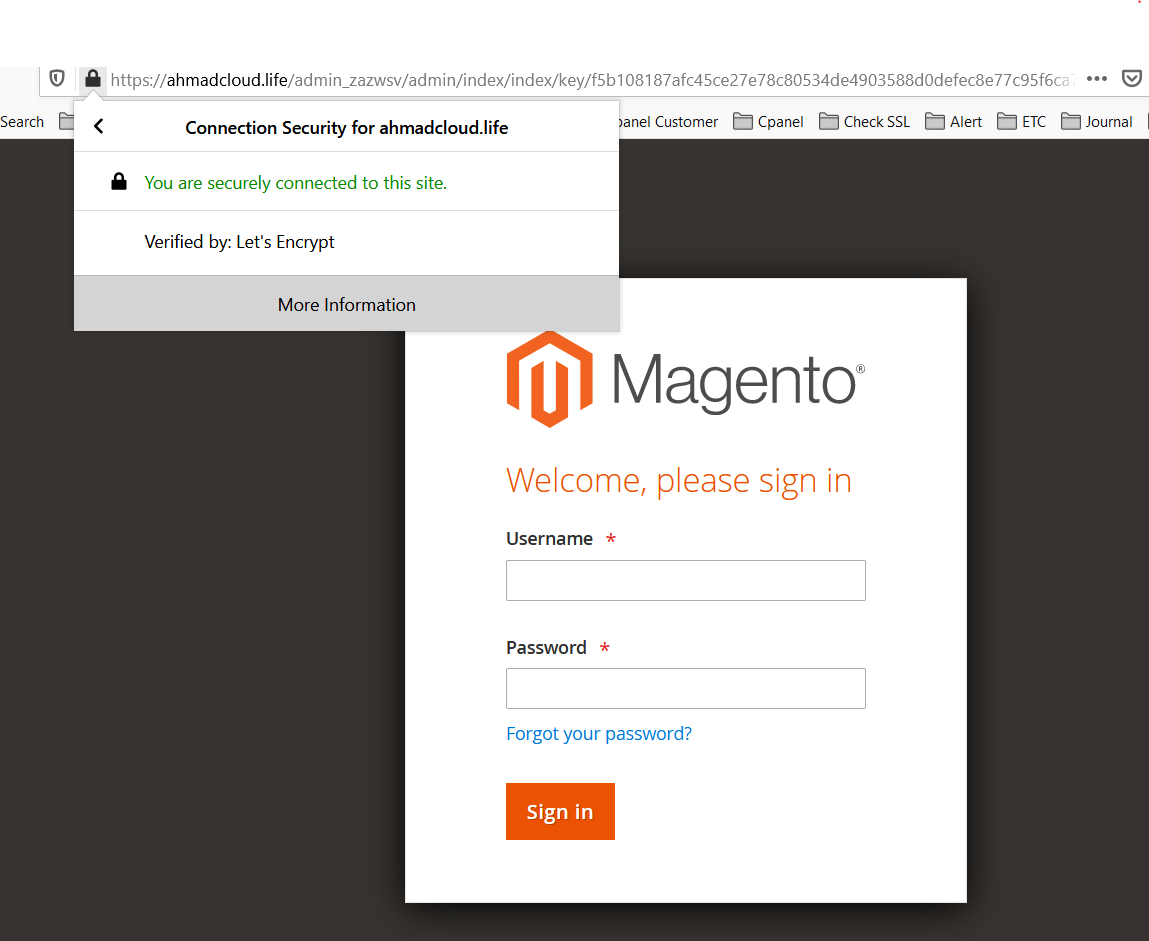
NOTE: IF YOU HAVE AN ISSUE WITH A TWO-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION STEPS, YOU CAN DISABLE THE MODULE HERE.
After this section you should be able to access Magento from your domain. (e.g https://ahmadcloud.life/admin_zazwsv)