-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
Have you ever saved your data without the ability to configure it in a more customizable way and free? It must be hard, isn’t it?
One of the solutions in managing our data in a more advanced and safer way is by using NextCloud.
What is NextCloud?
In short, NextCloud is an open-source platform for cloud storage solutions that allow users to self-host. Functionally it is similar to cloud storage solution that we often hear and of course, most of us have used them (Dropbox, Google Drive, One Drive, etc.).
Unlike other cloud providers, NextCloud gives more concern to our data privacy. Besides that, NextCloud can be installed on our on-premise server or in private virtual server (Cloud Raya’s VM for example). By that, we have more control over our data.
We are also able to upload files to our NextCloud and then synchronize the files to our computer, laptop, or smartphone.
NextCloud also provides many additional extension apps, making it more useful than just cloud storage.
The Impact and Benefit from Using NextCloud
There are many impacts and benefits that we can get by using NextCloud, they are:
- Full control of our infrastructure
- Accessible from all devices, anywhere
- Groupware, sharing files within users or groups will be so much easier and well-controlled
- Reliable and safe
- All-in-one-platform (file, address, calendar, chat, edit, email)
- Open-source and free
- End-to-end encryption, meaning the file can be encrypted in client’s device before uploaded to the server. So, even when someone tried to breach our server, they could not read our file.
When Do We Need NextCloud Solution?
From the benefits mentioned, these are the right moments for us using NextCloud:
- When cyber security becomes your main concern
- If you want to have alternative media for your main public cloud storage
- When you need more control of your data
- When you want to handle the limitation of scalability
Cloud Raya x NextCloud
Deploying NextCloud in Cloud Raya’s VM will give many benefits and advantages to you, they are:
- Helps you to manage cloud storage in a much easier way
- Enjoy the best time to use NextCloud and Cloud Raya’s user-friendly panel
- Increase your storage capacity easier needs anytime
- Advance security with Cloud Raya’s Security Profile
- Responsive support from Cloud Raya’s support team who is always ready to help
System & Specification Requirements
There are several requirements that are recommended by NextCloud to be followed so the performance, stability, and functionality can run well:
- OS: Ubuntu 20.04 lts (recommended)
- Database: MySQL 8.0+ or MariaDB 10.2/10.3/10.4/10.5 (recommended)
- Webserver: Apache 2.4 with mod php or php-fpm (recommended)
- PHP Runtime: 7.4, 8.0, 8.1 (recommended)
The system’s Requirement specification in running NextCloud’s server varies depending on the total user, application, file, and server’s activity volume.
Though NextCloud needs a minimum of 128MB RAM, but NextCloud recommends us if we have minimum 512MB RAM in our system.
For the number of CPU, can be started with 1 CPU, but also can use minimum 2 CPU if the number of users and workloads is increasing.
Install NextCloud in Cloud Raya
There are several steps that we should take before installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya’s VM.
1. Prepare VM
First, prepare VM in Cloud Raya. For this article I will use VM with this specification:
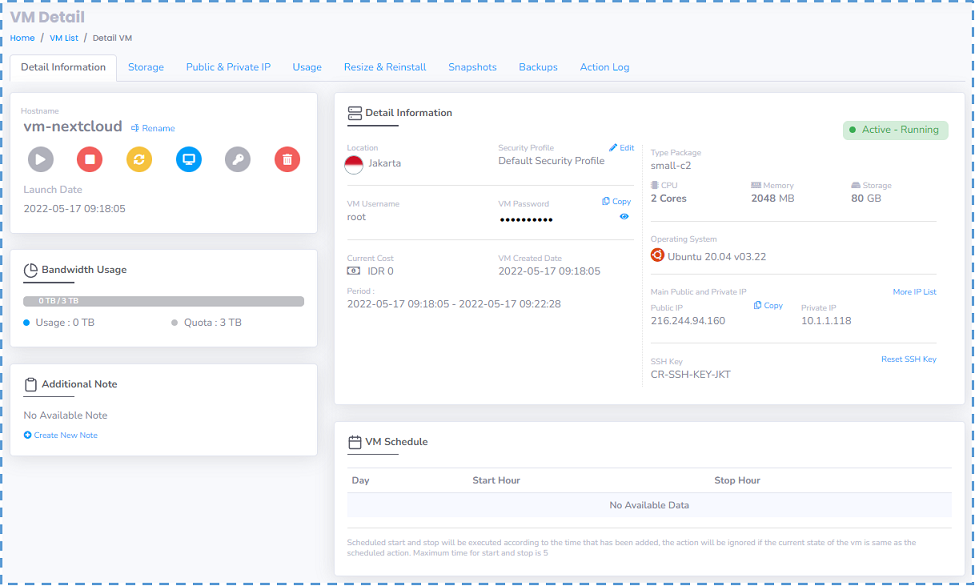
- Linux Ubuntu 20.04
- 2 Core CPU
- 2GB RAM
2. Ubuntu Software Packages Updates
Access the VM, then we have to update the repository and software package first
#sudo apt update #sudo apt upgrade 3. Install LAMP Stack (Apache MariaDB PHP)
Because NextCloud is written in PHP, so they need to install LAMP Stack first in our Ubuntu VM.
Install Apache Web Server
Insert this command:
#sudo apt install -y apache2 apache2-utils↳ Apache20-utils command will install some utilities that can be useful, like Apache HTTP Server Benchmarking Tool and etc.
After finishing the installation, Apache must be automatically turned on, we can check the status with systemcl.
#systemctl status apache2 Use this command to let the Apache always on automatically:
#sudo systemctl enable apache2 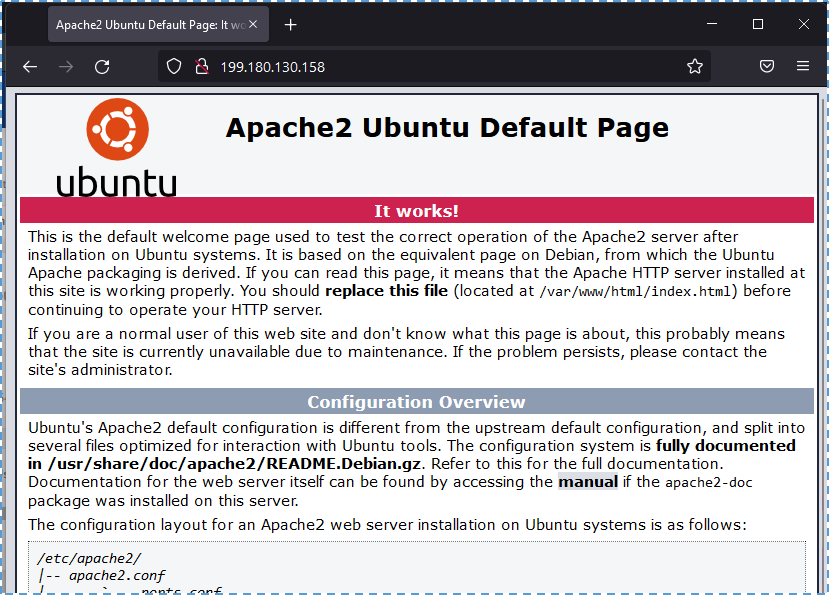
↳ Now we access the public IP from our VM in a browser, there should appear a default page from Apache2 Ubuntu.
Now we need to set www-data (Apache user) as owner of a web root, because in default, web root is owned by the root user. Use this command:
#sudo chown www-data:www-data /var/www/html/ -R Install MariaDB Database Server
In this article we will use MariaDB as server database. Insert this command to install it:
#sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client After installing, MariaDB will automatically be active, we can check the status with systemctl
#systemctl status mariadb Use this command to make MariaDB always automatically active on every system booting:
#sudo systemctl enable mariadb Now we run the post-installation security script
#sudo mysql_secure_installation 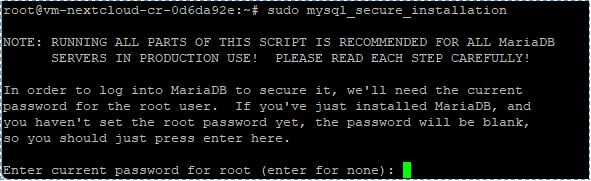
↳ When we asked to insert root password from MariaDB, we only need to click Enter because we just installed MariaDB. Then, push the Y button to start set root password.
For further steps, you can look into this image below:
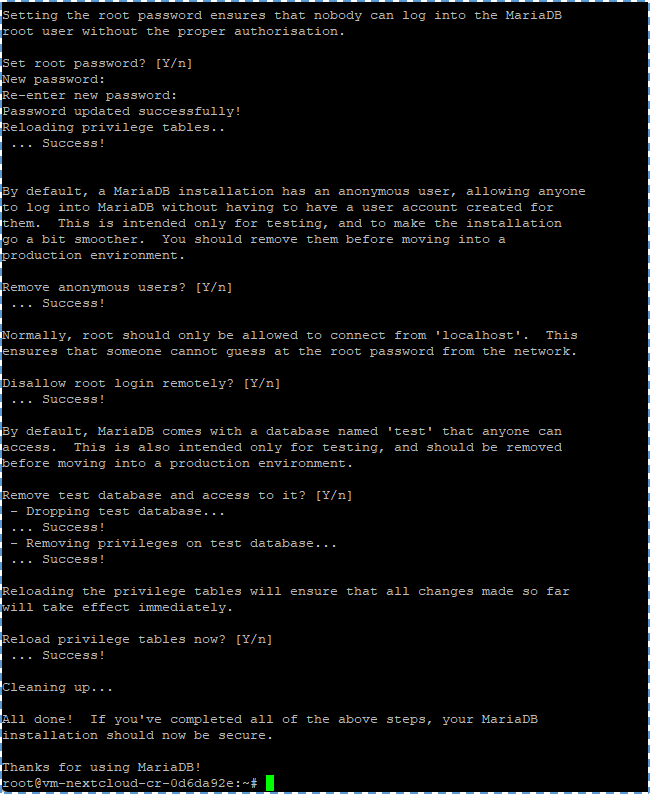
In default, MariaDB’s package in Ubuntu uses unix_socket to authenticate user login. In other words, we can use user pass from OS for login to MariaDB’s console. So, we can run the command to login without having to insert password root from MariaDB.
#sudo mariadb -u root 
Installing PHP
In this article I will be using version 7.4 which is a stable version of PHP and so far running smoothly with NextCloud. Enter the following command to install php and some common PHP modules.
#sudo apt install php7.4 libapache2-mod-php7.4 php7.4-mysql php-common php7.4-cli php7.4-common php7.4-json php7.4-opcache php7.4-readline Activate the PHP’s module and then restart Apache Web Server.
#sudo a2enmod php7.4 #sudo systemctl restart apache2 We also can check the information of PHP by giving below command.
#php -–version 
4. Installing NextCloud
Okay, after LAMP stack is installed in our VM, now we can move to the NextCloud installation and configure some of the essential things so that NextCloud can runs well.
Download NextCloud in Ubuntu
In the terminal, insert this command to download the newest version from NextCloud.
#wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/latest.zip Once the download is finished, extract this archieve by using package unzip. Then we can process the package installation.
#sudo apt install unzip #sudo unzip latest.zip -d /var/www/ ↳ –d option in the command functioned to decide the target directory. Meaning, the NextCloud files will be extracted to /var/www/nextcloud/.
After that we need to change the owner from this directory to www-data so that the web server (Apache) can access and write to this directory.
#sudo chown www-data:www-data /var/www/nextcloud/ -R Making Database and user for NextCloud in MariaDB
Log in to MariaDB
# sudo mariadb -u root Then we make a database for NextCloud. For this article I will add the database that is nextcloud_db. You can customize it into your needs.
create database nextcloud_db; 
Now let’s make user for this database, you can set username and password based on your needs.
create user admin@localhost identified by 'password-anda'; 
The last step, give this user all the privileges in the NextCloud database.
grant all privileges on nextcloud_db.* to admin@localhost identified by 'password-anda'; flush privileges; 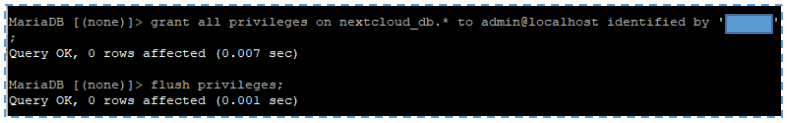
Then, insert exit as the command.
exit; Create Apache Virtual Host for NextCloud
We need to create and edit the file nextcloud.conf from /etc/apache2/sites-available/ directory.
#sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/nextcloud.conf Then, copy-paste this text below into a file. After that, save the file.
| <VirtualHost *:80> DocumentRoot “/var/www/nextcloud” ServerName files.tiyanwants.website ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/nextcloud.error CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/nextcloud.access combined <Directory /var/www/nextcloud/> Require all granted Options FollowSymlinks MultiViews AllowOverride All <IfModule mod_dav.c> Dav off </IfModule> SetEnv HOME /var/www/nextcloud SetEnv HTTP_HOME /var/www/nextcloud Satisfy Any </Directory> </VirtualHost> |
I will use files.tiyanwants.website as the domain in this article. You can always suit your needs. And of course, don’t forget to add DNS A record for this domain inside your DNS Zone editor.
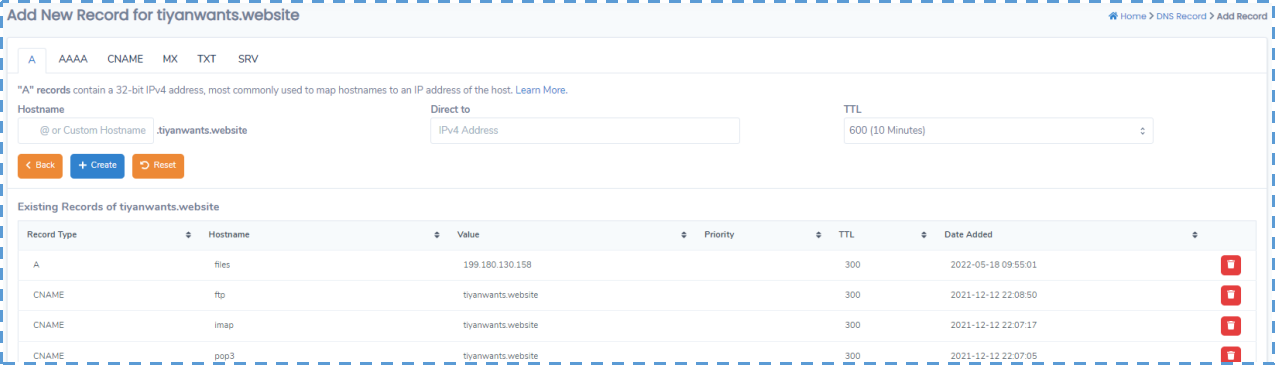
After that, activate this virtual host.
#sudo a2ensite nextcloud.conf Run this command to activate the Apache module you need
#sudo a2enmod rewrite headers env dir mime setenvif ssl Lastly, restart Apache to deploy the changes.
#sudo systemctl restart apache2 Install and Activate PHP Modul
Run this command for PHP module installation that is required and recommend by NextCloud.
#sudo apt install imagemagick php-imagick libapache2-mod-php7.4 php7.4-common php7.4-mysql php7.4-fpm php7.4-gd php7.4-json php7.4-curl php7.4-zip php7.4-xml php7.4-mbstring php7.4-bz2 php7.4-intl php7.4-bcmath php7.4-gmp Reload Apache to activate this module with below command
#sudo systemctl reload apache2 Activate HTTPS
At this point, we should be able to access NextCloud web install wizard in our browser.
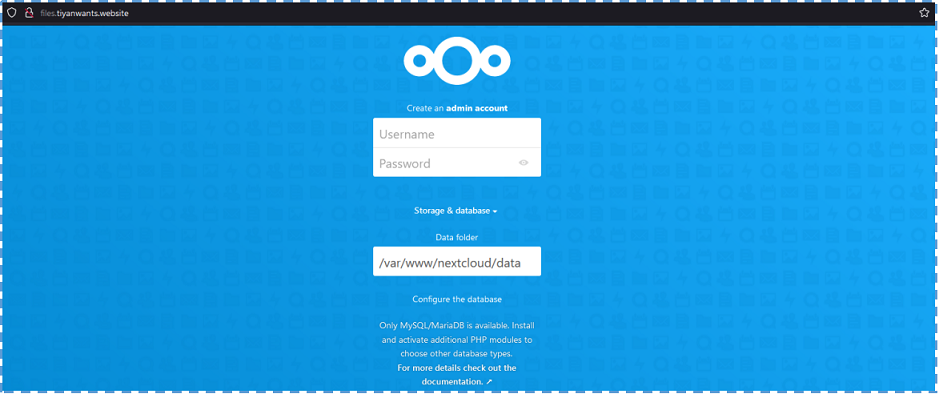
But before entering sensitive information, it will be better to activate HTTPS inside our NextCloud domain.
#sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-apache ↳ Python3-certbot-apache is an Apache plugins.
Run belows command to get free TLS certificate using Apache Plugin.
#sudo certbot --apache --agree-tos --redirect --staple-ocsp --email wisesa.tiyan@gmail.com -d files.tiyanwants.website Where:
- –apache2: use Apache’s authenticator and installation
- –agree-tos: Agree to Let’s Encrypt service requirement
- –redirect: Implement HTTPS by adding 301 redirect
- –staple-ocsp: Activate Stapel OCSP
- –email: Email used for registration and recovery contact
- -d is followed by a list of domain names, separated by commas. You can add up to 100 domain names
There will be some options that we need to fill. Once it finishes, TLS certification will automatically obtain and configured for us, it shows by the message below.
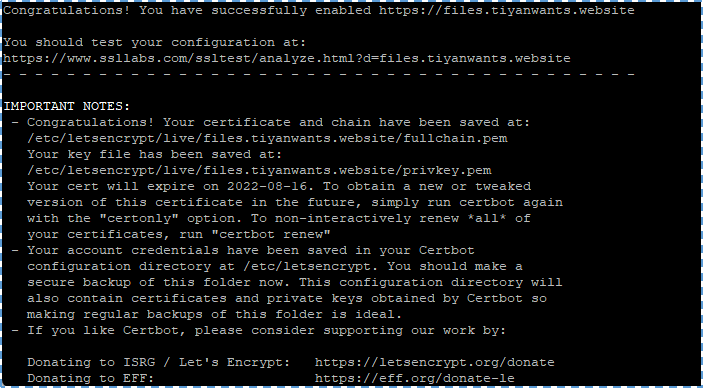
The next configuration is to enable HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security). Because sometimes Certbot can’t automatically add HSTS header in Apache configuration file for NextCloud. Let’s edit this file first.
#sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/nextcloud-le-ssl.conf Then, add this line to SSL server block to activate HSTS header.
Header always set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000" 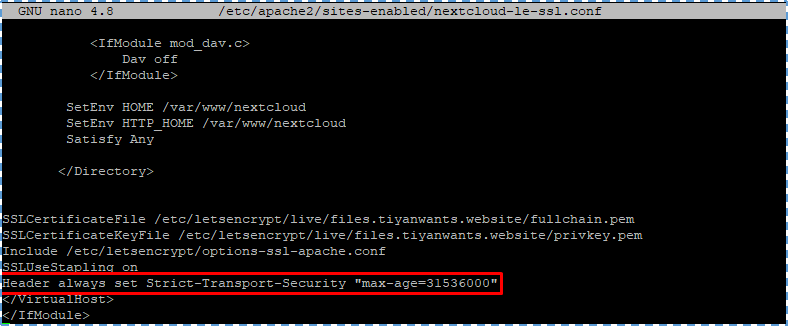
Lastly, restart Apache so the changes will be successfully implemented.
#sudo systemctl reload apache2 Cloud Finalization
Now when we want to access our NextCloud dashboard, we are automatically use HTTPS.
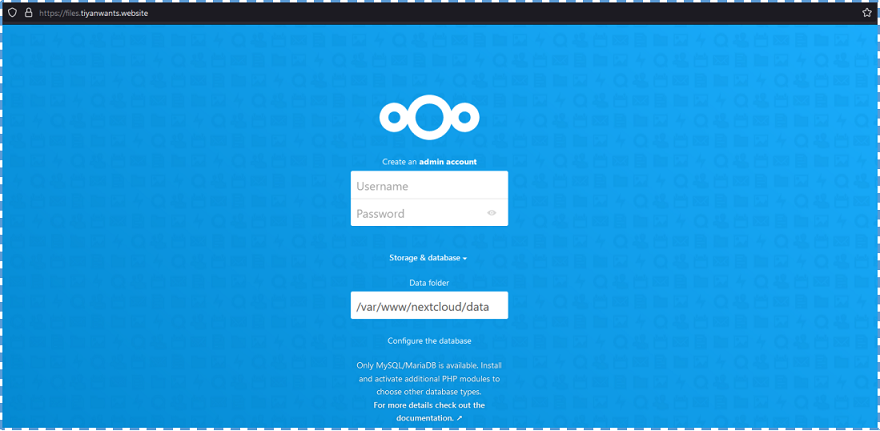
To finish the installation, in this wizard page we need to do several things:
- Create admin account
- Decide NextCloud’s data folder location
- entering database detail that have been made in step 2, and
- Decide the host address
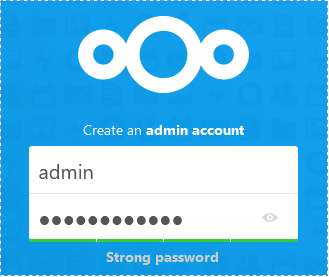
↳ Input username and password for admin user.
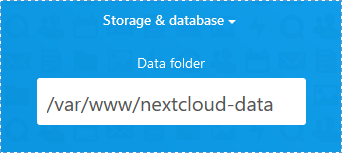
↳ Data folder is a place where the user’s file being saved. It would be better to place data directory outside of webroot directory from NextCloud. Instead of saving the users file in /var/www/nextcloud/data/, we can change it to /var/www/nextcloud-data.
To do it, we can do it with this command
#sudo mkdir /var/www/nextcloud-data Then, make sure Apache’s user (www-data) has the permission to write into the data directory.
#sudo chown www-data:www-data /var/www/nextcloud-data -R 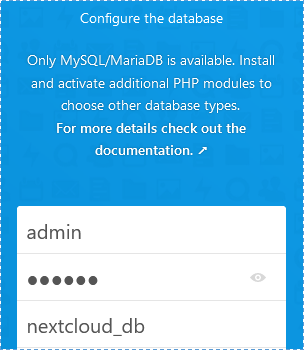
↳ Re-input the database detail that we have made on previous steps.
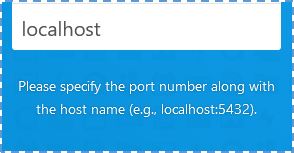
↳ We can use default localhost as host address, or we can input localhost:3306, because MariaDB use port 3306.
After that, click “install”. Then we will be redirected to the main page of NextCloud’s dashboard.
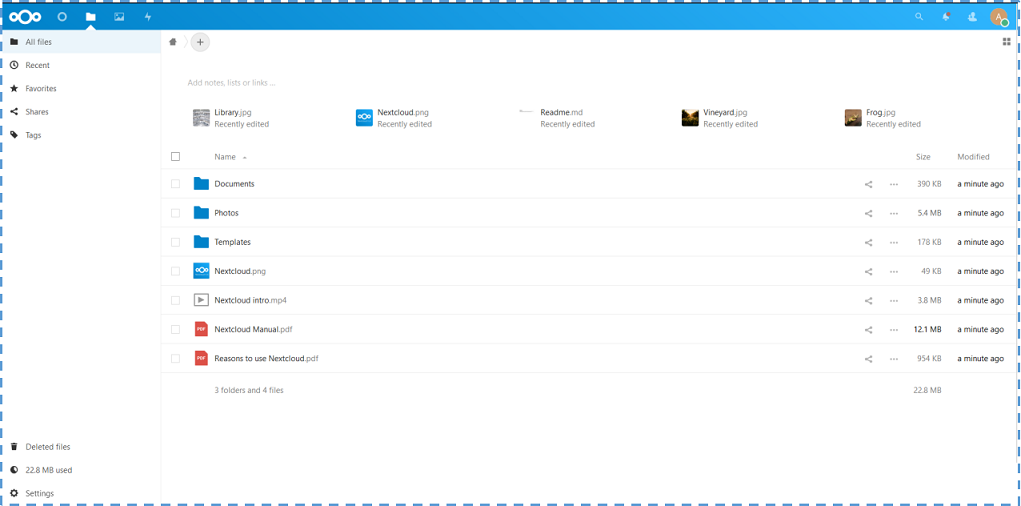
Okay, now we can use NextCloud as our Private Cloud Storage.
5. Essential Additional Configuration
Increase PHP Memory Limit
The default limitation of PHP memory is 128MB, but NextCloud recommend 512MB for better performance. To change PHP memory limit, edit this PHP file,
#sudo nano /etc/php/7.4/apache2/php.ini Direct to this line
memory_limit = 128M Change the value into
memory_limit = 512M 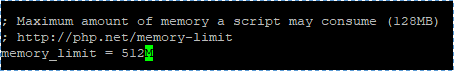
Save & close, then restart Apache so the company will implement the changes.
#sudo systemctl reload apache2 Configure Redis Cache for NextCloud
We will actvate the cache memory for NextCloud by using redis. Run this command to install Redis from Ubuntu repositoory.
#sudo apt install redis-server To configure Redis as cache for NextCloud, we need to install PHP extension so it can interact with Redis.
#sudo apt install php-redis Next, edit NextCloud’s file configuration.
#sudo nano /var/www/nextcloud/config/config.php Add the following line before the end. );
| ‘memcache.distributed’ => ‘\OC\Memcache\Redis’, ‘memcache.local’ => ‘\OC\Memcache\Redis’, ‘memcache.locking’ => ‘\OC\Memcache\Redis’, ‘redis’ => array( ‘host’ => ‘localhost’, ‘port’ => 6379, ), |
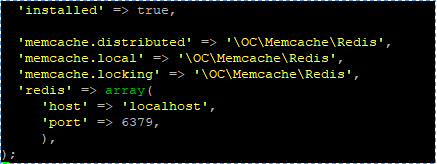
Save and close file. Then, restart Apache and PHP-FPM.
#sudo systemctl restart apache2 Case Study
Okay, after we have successfully installed NextCloud in the VM, let’s try to make a case study in using NextCloud. With the following case studies:
- Have 2 group of divisions
a. Sales
b. Billing
- Will choose one divisions leader to manage the group.
- Making “file-sharing” based on the groups. However, the Customer’s Invoice file from Billing division, is shared with the Sales Division as well.
Let’s see these steps to achieve the goal.
↳ First, access Users menu
↳ Then, click Add Group, and input the group’s name.
↳ Now we are adding new users then deciding which group the new user belongs to.
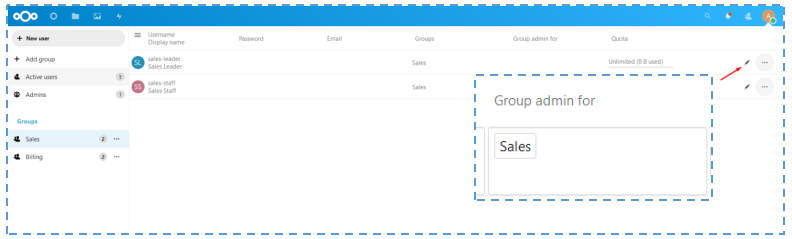
↳ In Active Users menu, edit the user that will become the administrator for the group’s division.
↳ After that, now let’s switch account to one of the users that we have been made, then access menu File.
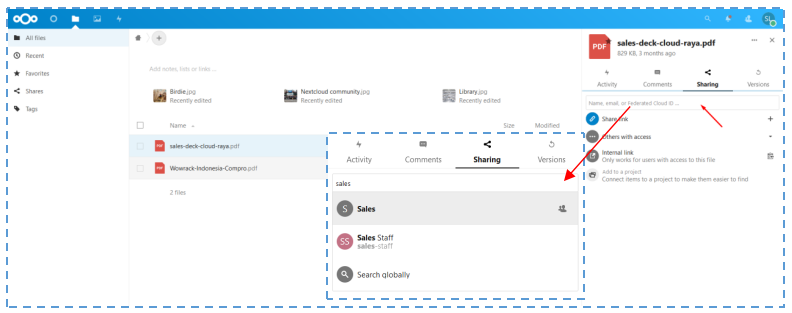
↳ Decide which file that we will share and choose the group. In the Sharing tab, decide which group will be shared the file with.
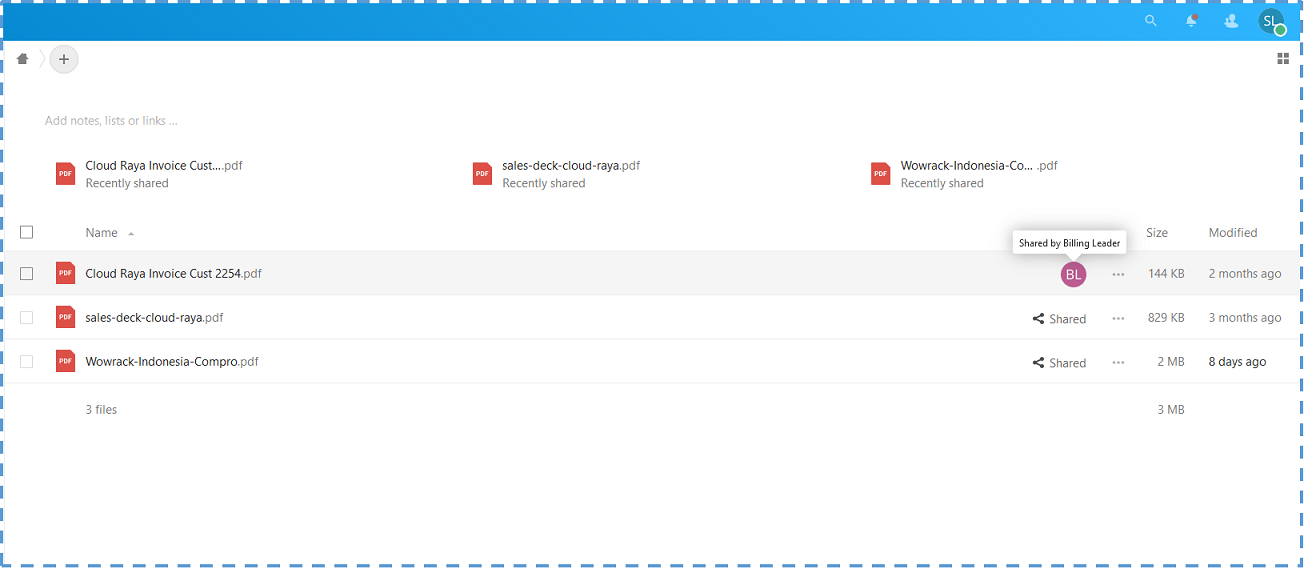
↳ We can see the file shared by the Billing gorup to Sales group also appear inside the file list.
Conclusion
From this article we learned together how to install NextCloud. Starting from how to install it on Cloud Raya’s VM, its configuration, to the case study examples in it.
If you want to see the video tutorial version, you can access it in Cloud Raya’s Youtube channel or through this link.
For questions or discussions about this tutorial, you can directly submit them in the comments column.