-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
Nextcloud is an open-source file-sync and file collaboration server which can be used for self-host. It also comes with an Enterprise Edition with enterprise support.
There are various methods to deploy Nextcloud :
- Manual install
- Docker image
- Web installer
This article will guide you on how to install Nextcloud in Cloud Raya using Manual install and Docker.
Server Requirements
Server OS:
- Ubuntu 20.04 LTS (recommended)
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 (recommended)
- Debian 10 (Buster)
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15
- openSUSE Leap 42.1+
- CentOS 8
Database:
- MySQL 8.0+ or MariaDB 10.2+ (recommended)
- Oracle Database 11g (only as part of an enterprise subscription)
- PostgreSQL 9.6/10/11/12/13
- SQLite (only recommended for testing and minimal-instances)
PHP runtime:
- 7.3
- 7.4 (recommended)
Manual Installation
Preparation
This section will guide you on how to prepare your server before it will get installed with Nextcloud.
Assuming that you’ve already installed and configured the server with LEMP stack. However, if you haven’t, you can read the following articles:
For RHEL 8 / CentOS 8, make sure you have turned off SELinux.
Make sure you are already allowed port 80 and 443 globally in your Security Profile.
Getting Nextcloud Package
Get the latest Nextcloud package from here: https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/latest.tar.bz2
The above link will always point to the latest version of Nextcloud. But if you wish to install a specific version, you can find it here: https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/
Download the file using curl
cd
curl -O https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/latest.tar.bz2Then extract it to somewhere you wish, but by default it usually goes to /var/www/, for Ubuntu 20.04:
cd
tar -C /var/www -xvf latest.tar.bz2For RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 , you will need to install bzip2 package first:
dnf install bzip2 -y
mkdir -p /var/www
tar -C /var/www -xvf latest.tar.bz2Next, you need to change the owner of the extracted Nextcloud folder. It must be matched with the user, defined in the web server settings. The default user on Ubuntu is www-data, on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 however, you will have to match the ownership as the web server you are using, either apache or nginx.
chown -R www-data.www-data /var/www/nextcloud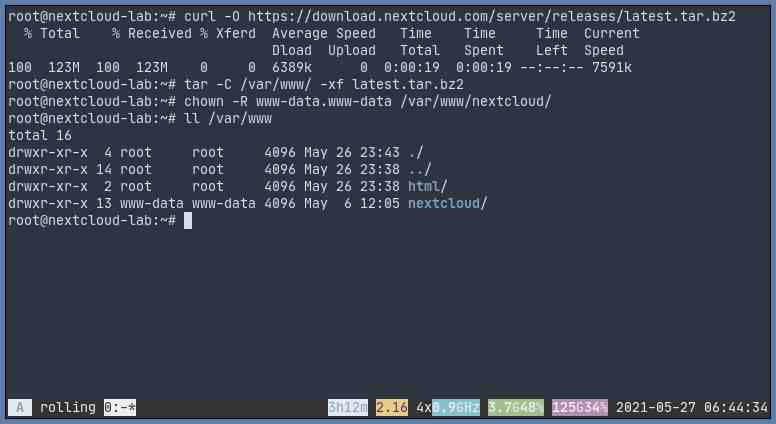
Creating Database and Database User
Create a database and a database user for our Nextcloud instance.
mysql -uroot -p
CREATE DATABASE nextclouddb;
CREATE USER 'dbuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON nextclouddb.* TO 'dbuser'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;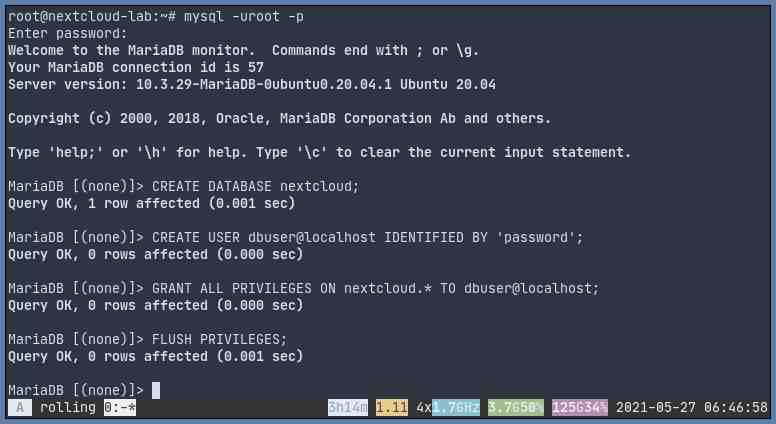
PHP Modules
Install the following PHP 7.4 modules
Ubuntu 20.04
apt install php7.4-common php7.4-curl php7.4-gd php7.4-gd php7.4-json php7.4-xml php7.4-mbstring php7.4-zip php7.4-mysql php7.4-gmp php7.4-ldap php7.4-bcmath php7.4-bz2 php7.4-imap php7.4-intl php7.4-apcu php7.4-imagick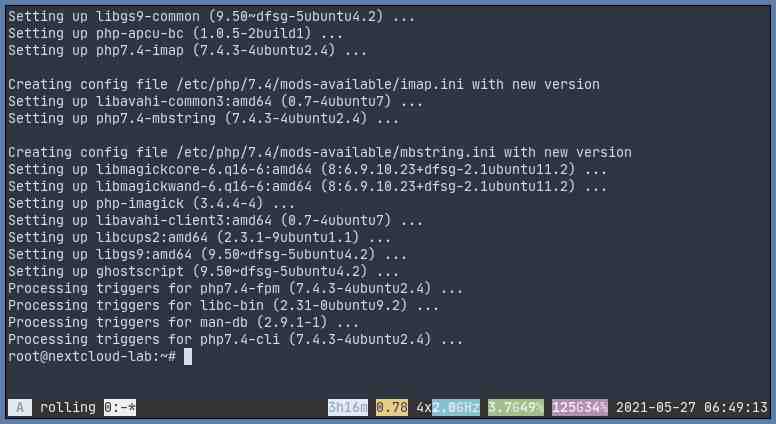
RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
Don’t forget to enable PHP 7.4 module
dnf module enable php:7.4
dnf install php-common php-curl php-gd php-json php-xml php-mysqlnd php-mbstring php-zip php-gmp php-ldap php-bcmath php-bz2 php-intl php-apcu php-imagickPHP Configuration
Modify the following lines in your www.conf. For Ubuntu 20.04, it should be located in /etc/php/7.4/fpm/pool.d/www.conf and for RHEL 8 / CentOS 8, it’s normally located in /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
;env[HOSTNAME] = $HOSTNAME
;env[PATH] = /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin
;env[TMP] = /tmp
;env[TMPDIR] = /tmp
;env[TEMP] = /tmpMake sure those lines are uncommented.
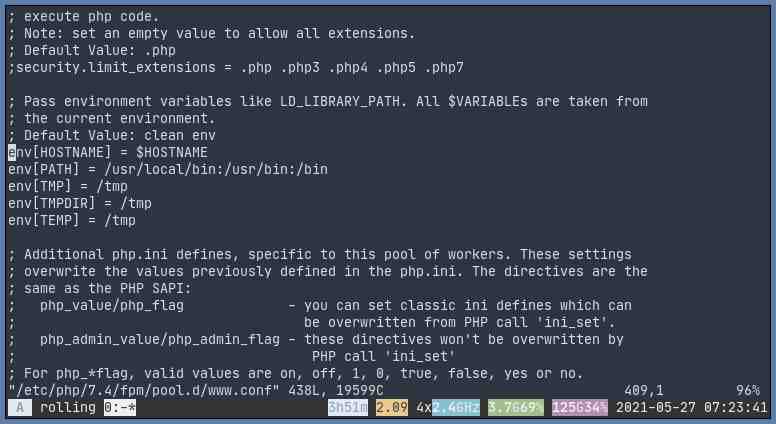
Then restart php-fpm
Ubuntu : systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
RHEL 8 / CentOS 8 : systemctl restart php-fpm
Webserver – Nginx
You need to create a new server block for nextcloud.conf which will serve Nextcloud files.
upstream php-handler {
#server 127.0.0.1:9000;
server unix:/var/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock;
}
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name cloud.example.com;
# Enforce HTTPS
return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name cloud.example.com;
# Use Mozilla's guidelines for SSL/TLS settings
# <https://mozilla.github.io/server-side-tls/ssl-config-generator/>
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/nginx/cloud.example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/nginx/cloud.example.com.key;
# HSTS settings
# WARNING: Only add the preload option once you read about
# the consequences in <https://hstspreload.org/>. This option
# will add the domain to a hardcoded list that is shipped
# in all major browsers and getting removed from this list
# could take several months.
#add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=15768000; includeSubDomains; preload;" always;
# set max upload size
client_max_body_size 512M;
fastcgi_buffers 64 4K;
# Enable gzip but do not remove ETag headers
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_min_length 256;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private no_last_modified no_etag auth;
gzip_types application/atom+xml application/javascript application/json application/ld+json application/manifest+json application/rss+xml application/vnd.geo+json application/vnd.ms-fontobject application/x-font-ttf application/x-web-app-manifest+json application/xhtml+xml application/xml font/opentype image/bmp image/svg+xml image/x-icon text/cache-manifest text/css text/plain text/vcard text/vnd.rim.location.xloc text/vtt text/x-component text/x-cross-domain-policy;
# Pagespeed is not supported by Nextcloud, so if your server is built
# with the `ngx_pagespeed` module, uncomment this line to disable it.
#pagespeed off;
# HTTP response headers borrowed from Nextcloud `.htaccess`
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header X-Download-Options "noopen" always;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies "none" always;
add_header X-Robots-Tag "none" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
# Remove X-Powered-By, which is an information leak
fastcgi_hide_header X-Powered-By;
# Path to the root of your installation
root /var/www/nextcloud;
# Specify how to handle directories -- specifying `/index.php$request_uri`
# here as the fallback means that Nginx always exhibits the desired behaviour
# when a client requests a path that corresponds to a directory that exists
# on the server. In particular, if that directory contains an index.php file,
# that file is correctly served; if it doesn't, then the request is passed to
# the front-end controller. This consistent behaviour means that we don't need
# to specify custom rules for certain paths (e.g. images and other assets,
# `/updater`, `/ocm-provider`, `/ocs-provider`), and thus
# `try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$request_uri`
# always provides the desired behaviour.
index index.php index.html /index.php$request_uri;
# Rule borrowed from `.htaccess` to handle Microsoft DAV clients
location = / {
if ( $http_user_agent ~ ^DavClnt ) {
return 302 /remote.php/webdav/$is_args$args;
}
}
location = /robots.txt {
allow all;
log_not_found off;
access_log off;
}
# Make a regex exception for `/.well-known` so that clients can still
# access it despite the existence of the regex rule
# `location ~ /(\\.|autotest|...)` which would otherwise handle requests
# for `/.well-known`.
location ^~ /.well-known {
# The following 6 rules are borrowed from `.htaccess`
rewrite ^/\\.well-known/host-meta\\.json /public.php?service=host-meta-json last;
rewrite ^/\\.well-known/host-meta /public.php?service=host-meta last;
rewrite ^/\\.well-known/webfinger /public.php?service=webfinger last;
rewrite ^/\\.well-known/nodeinfo /public.php?service=nodeinfo last;
location = /.well-known/carddav { return 301 /remote.php/dav/; }
location = /.well-known/caldav { return 301 /remote.php/dav/; }
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
# Rules borrowed from `.htaccess` to hide certain paths from clients
location ~ ^/(?:build|tests|config|lib|3rdparty|templates|data)(?:$|/) { return 404; }
location ~ ^/(?:\\.|autotest|occ|issue|indie|db_|console) { return 404; }
# Ensure this block, which passes PHP files to the PHP process, is above the blocks
# which handle static assets (as seen below). If this block is not declared first,
# then Nginx will encounter an infinite rewriting loop when it prepends `/index.php`
# to the URI, resulting in a HTTP 500 error response.
location ~ \\.php(?:$|/) {
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+?\\.php)(/.*)$;
set $path_info $fastcgi_path_info;
try_files $fastcgi_script_name =404;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $path_info;
fastcgi_param HTTPS on;
fastcgi_param modHeadersAvailable true; # Avoid sending the security headers twice
fastcgi_param front_controller_active true; # Enable pretty urls
fastcgi_pass php-handler;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
fastcgi_request_buffering off;
}
location ~ \\.(?:css|js|svg|gif)$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
expires 6M; # Cache-Control policy borrowed from `.htaccess`
access_log off; # Optional: Don't log access to assets
}
location ~ \\.woff2?$ {
try_files $uri /index.php$request_uri;
expires 7d; # Cache-Control policy borrowed from `.htaccess`
access_log off; # Optional: Don't log access to assets
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$request_uri;
}
}You’ll need to adjust the server_name to match your own domain, and don’t forget to fix the SSL certificate and key location as well. You may also need to modify the php-fpm configuration, either you use a Unix socket or not.
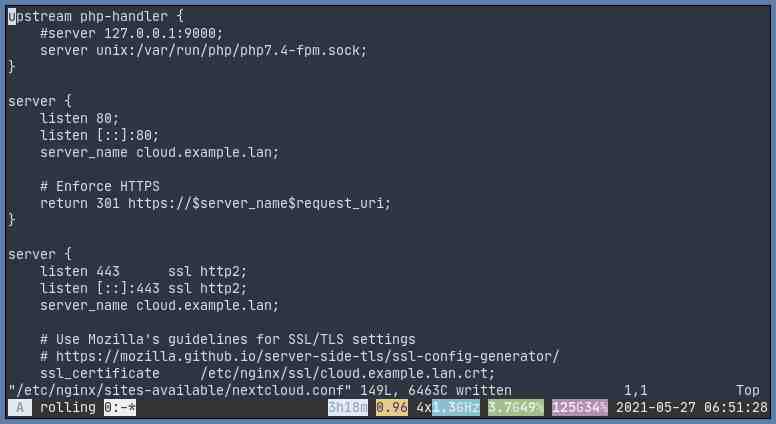
For the certificate, you might want to put your commercially signed certificate or just use letsencrypt or even a self-signed one. Here’s how to generate self-signed certificate: LINK
Ubuntu 20.04
Place the configuration on /etc/nginx/sites-available then you’ll have to do this to activate it:
cd /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
ln -s ../sites-available/nextcloud.conf .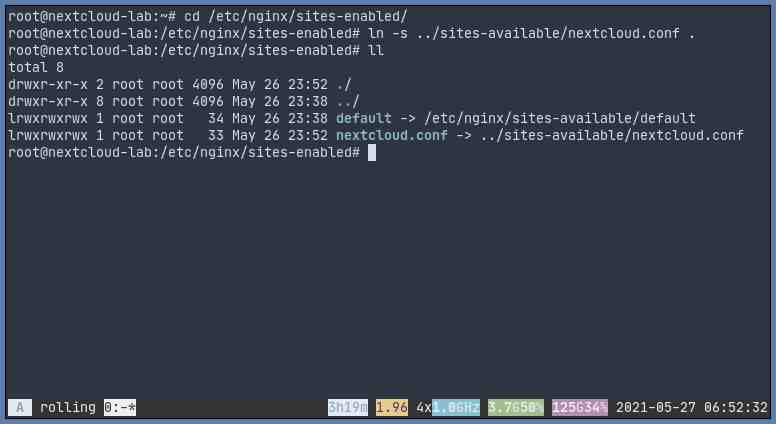
RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
Put the configuration on /etc/nginx/conf.d/
Then make sure that the configuration is correct and then reload nginx:
# check configurations
nginx -t
# reload nginx
nginx -s reloadFor RHEL 8 / CentOS 8, you might need to adjust your php-fpm configuration if it’s not done yet. Find the below lines in /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf and change the values accordingly:
..
user = nginx
group = nginx
..
listen.owner = nginx
listen.group = nginx
..Later on, after Nextcloud installation, if you encounter a login redirect loop, you might want to check the ownership of /var/lib/php/session to make sure it’s owned by nginx group at least.
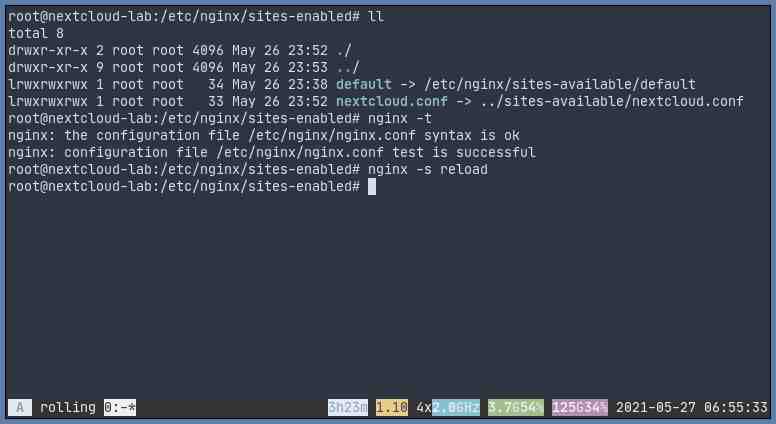
Installing Nextcloud
Open your browser and access your predefined domain. Mine was https://cloud.example.lan. Then fill out the fields with the required data. For the Data Folder field, if you’re unsure, then just leave it untouched.
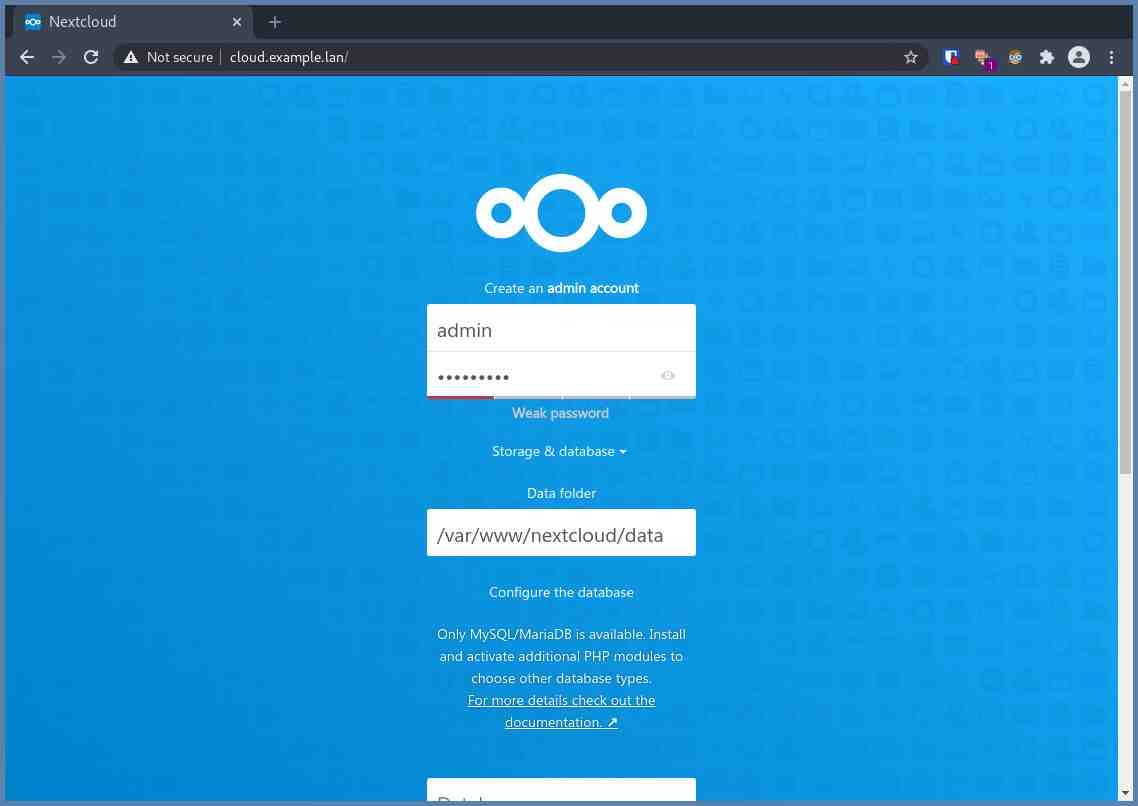
After filling out everything, then click Finish setup.
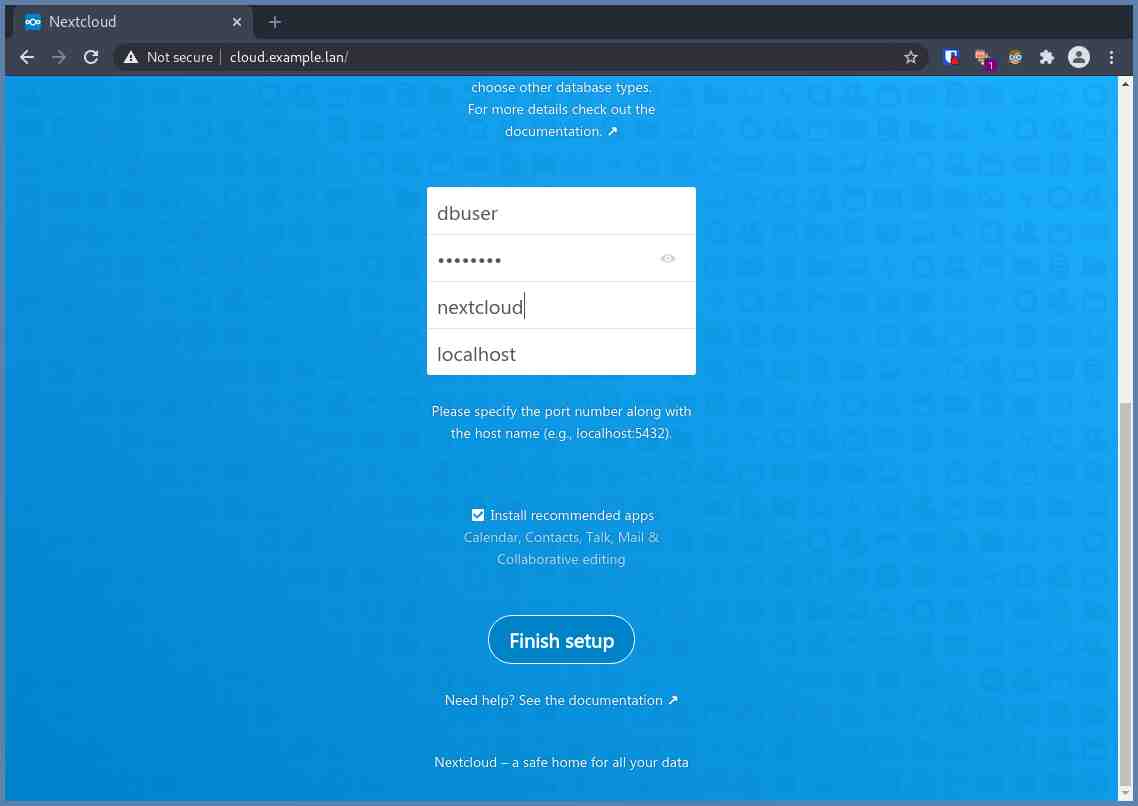
Wait for the installation and pay attention, do not close this tab / browser until the installation finishes.
Last thing to do is go to https://YOUR_NEXCLOUD_DOMAIN/settings/admin/overview and do what the checklist says. It’s to make sure that your setup is complete.
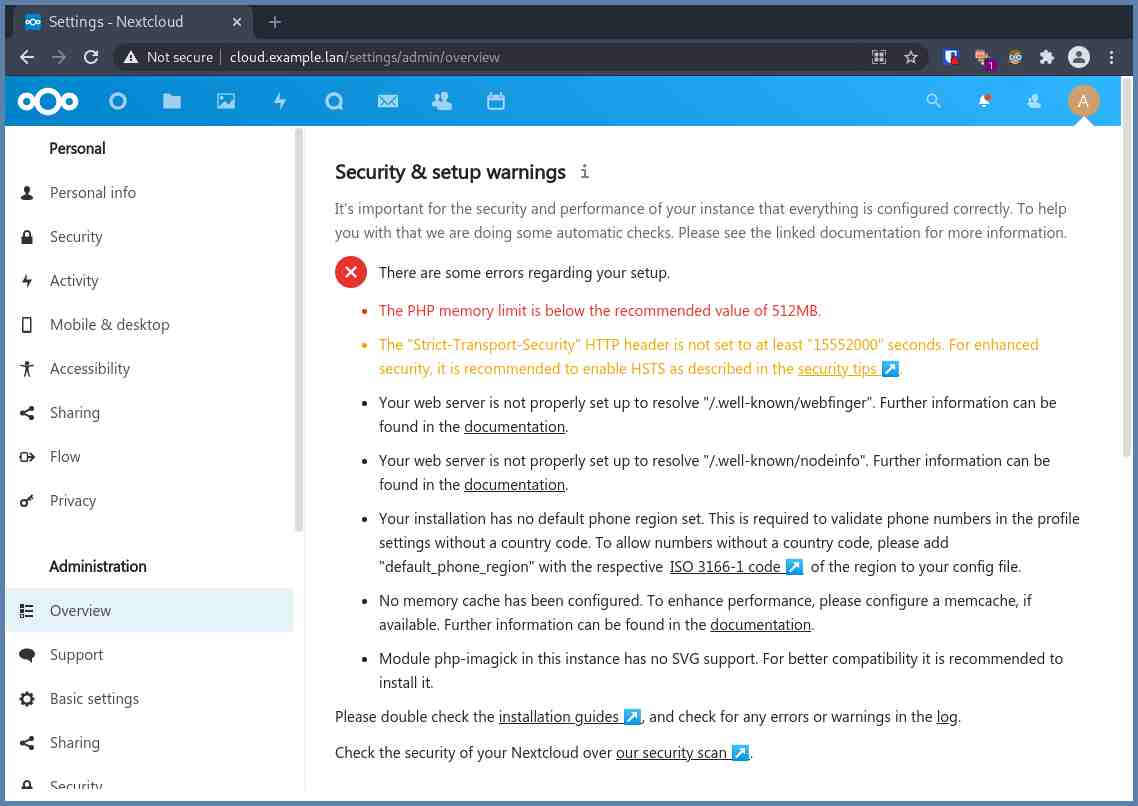
Once you complete them, then your Nextcloud is ready to be used! Yay
Docker Image
Deploying Nextcloud using Docker image is a lot easier than the manual one. Basically, you’ll just need to pull the nextcloud image then run it. That’s it.
Assuming that you already have docker installed on your machine. But if you haven’t yet, you can read the tutorial via this link.
Here’s how to deploy Nextcloud using Docker
Docker Compose (recommended)
Copy paste the following snippet and save it as docker-compose.yml
---
version: "2.1"
services:
nextcloud:
image: ghcr.io/linuxserver/nextcloud
container_name: nextcloud
environment:
- PUID=1000
- PGID=1000
- TZ=Asia/Jakarta
volumes:
- /path/to/appdata:/config
- /path/to/data:/data
ports:
- 443:443
restart: unless-stopped
Make sure you have adjusted the necessary values to match your environment.
Finally, run the below command to deploy it:
docker-compose up
Docker CLI
Using docker-compose is more preferred. You can easily make changes then redeploy the container. But if you prefer CLI way, here’s the snippet:
docker run -d \\
--name=nextcloud \\
-e PUID=1000 \\
-e PGID=1000 \\
-e TZ=Asia/Jakarta \\
-p 443:443 \\
-v /path/to/appdata:/config \\
-v /path/to/data:/data \\
--restart unless-stopped \\
ghcr.io/linuxserver/nextcloud
As always, you’ll have to modify some values to match you environment.
Installation
The installation process is the exact same as the manual approach.
If you need a thorough guide, you can read the official documentation here: https://docs.nextcloud.com/server/latest/admin_manual/contents.html