-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
PostgreSQL is a powerful OpenSource, an object-relational database management system that extends the SQL language with many features.
Meanwhile, Patroni is an OpenSource python package that we can use to manage and automate the deployment of PostgreSQL HA Clusters. Little information, Patroni was developed by Zalando.
Prerequisite
To follow this tutorial, we need three VM for PostgreSQL and one VM for HAproxy and etcd.
Below is four VMs that we will deploy in Cloud Raya.
| Hostname | IP Address | Applications |
| haetcd | 199.180.130.99 | HAproxy |
| 10.3.3.166 | etcd | |
| pgsql1 | 10.3.3.12 | patroni |
| pgsql2 | 10.3.3.71 | patroni |
| pgsql3 | 10.3.3.70 | patroni |
We will use haetcd as jumpbox server since the VM has Public IP Address that we can access from the outside network. In /etc/host, insert the hostname of the servers to make us easy to access the server without remembering the IP Address.
/etc/hosts
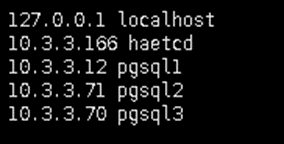
Install PostgreSQL 14
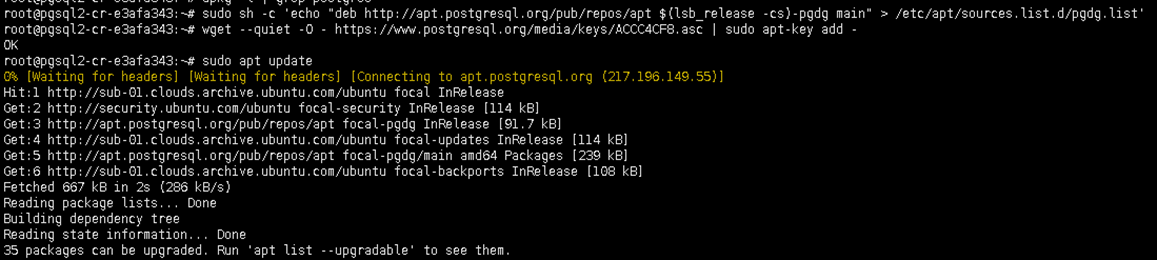
In this step, we will use PostgreSQL14 for pgsql1, pgsql2, and pgsql3. Please the command below on each server.
sh -c 'echo "deb http://apt.postgresql.org/pub/repos/apt $(lsb_release -cs)-pgdg main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pgdg.list'wget --quiet -O - https://www.postgresql.org/media/keys/ACCC4CF8.asc | sudo apt-key add - apt update
apt -y install postgresql-14 postgresql-server-dev-14
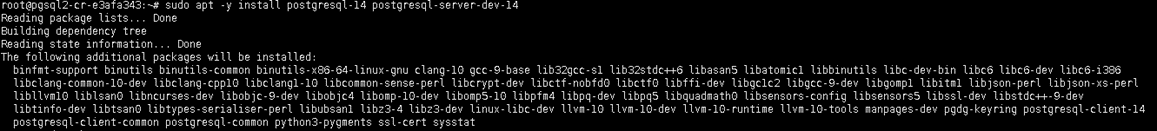
After the postgresql installation is completed, we need to stop and disable PostgreSQL service. Then we will continue to install patroni.
systemctl stop postgresql && systemctl disable postgresql
Install Patroni
Patroni uses the utilities of PostgreSQL that we have installed previously which is located at /usr/lib/postgresql/versin/bin directory.
In this step, we create a symbolic link to PostgreSQL utilities on psql1, psql2, and psql3
ln -s /usr/lib/postgresql/14/bin/* /usr/sbin/
Next, we will install patroni on each server
apt -y install python3 python3-pip
pip install --upgrade setuptools
pip install psycopg2
pip install patroni
pip install python-etcd
Configure Patroni on Pgsql1, Pgsql2, and Pgsql3
Patroni uses yaml files to store the configuration. We will place the yaml file on /etc directory.
sudo nano /etc/patroni.yml
pgsql1:
scope: postgres
namespace: /db/
name: pgsql1
restapi:
listen: 10.3.3.12:8008
connect_address: 10.3.3.12:8008
etcd:
host: 10.3.3.166:2379
bootstrap:
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
initdb:
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums
pg_hba:
- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.12/0 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.71/0 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.70/0 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb
postgresql:
listen: 10.3.3.12:5432
connect_address: 10.3.3.12:5432
data_dir: /data/patroni
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: replogin321
superuser:
username: postgres
password: secretlogin321
parameters:
unix_socket_directories: '.'
tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
pgsql2
scope: postgres
namespace: /db/
name: pgsql2
restapi:
listen: 10.3.3.71:8008
connect_address: 10.3.3.71:8008
etcd:
host: 10.3.3.166:2379
bootstrap:
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
initdb:
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums
pg_hba:
- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.12/0 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.71/0 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.70/0 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb
postgresql:
listen: 10.3.3.71:5432
connect_address: 10.3.3.71:5432
data_dir: /data/patroni
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: replogin321
superuser:
username: postgres
password: secretlogin321
parameters:
unix_socket_directories: '.'
tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
pgsql3
scope: postgres
namespace: /db/
name: pgsql3
restapi:
listen: 10.3.3.70:8008
connect_address: 10.3.3.70:8008
etcd:
host: 10.3.3.166:2379
bootstrap:
dcs:
ttl: 30
loop_wait: 10
retry_timeout: 10
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true
initdb:
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums
pg_hba:
- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.12/0 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.71/0 md5
- host replication replicator 10.3.3.70/0 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
users:
admin:
password: admin
options:
- createrole
- createdb
postgresql:
listen: 10.3.3.70:5432
connect_address: 10.3.3.70:5432
data_dir: /data/patroni
pgpass: /tmp/pgpass
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: replogin321
superuser:
username: postgres
password: secretlogin321
parameters:
unix_socket_directories: '.'
tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
According to the yml file, the data of PostgreSQL will be stored at /data/patroni. Make sure the ownership of that directory is postgres.
mkdir -p /data/patroni
chown postgres:postgres /data/patronichmod 700 /data/patroni
Create a Service
Next, we will create patroni service that allow us to start and stop the service on each server.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/patroni.service
Add the following parameter in the patroni.service
[Unit]
Description=High availability PostgreSQL Cluster
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=postgres
Group=postgres
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/patroni /etc/patroni.yml
KillMode=process
TimeoutSec=30
Restart=no
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Create and Enable Patroni Service
After the patroni service has been created then we enable it to make it autostart.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable patroni
Install Etcd and Haproxy on Haetcd VM
etcd is a fault-tolerant, a distributed key value store that can be used to store the state of PostgreSQL cluster. With etcd, it will keep the PostgreSQL cluster up and running.
Run the command below to install etcd
sudo apt -y install etcd
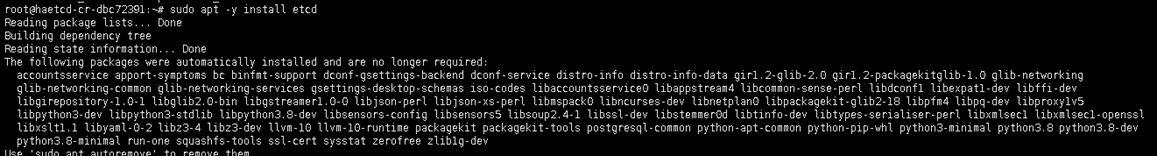
Next step, we will configure the etcd file. Add the below parameter in the etcd file:
sudo nano /etc/default/etcd
ETCD_LISTEN_PEER_URLS="http://10.3.3.166:2380"
ETCD_LISTEN_CLIENT_URLS="http://localhost:2379,http://10.3.3.166:2379"
ETCD_INITIAL_ADVERTISE_PEER_URLS="http://10.3.3.166:2380"
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER="default=http://10.3.3.166:2380"
ETCD_ADVERTISE_CLIENT_URLS="http://10.3.3.166:2379"
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER_TOKEN="etcd-cluster"
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER_STATE="new"
Restart the etcd service to make a change effect
sudo systemctl restart etcd
Start Patroni on Each Pgsql Server
Before we start the patroni service, we need to activate the watchdog support to prevent split-brain on the PostgreSQL
https://patroni.readthedocs.io/en/latest/watchdog.htmlmodprobe softdog
chown postgres /dev/watchdog

After the watchdog is activated, now we can start the patroni service again on each server.
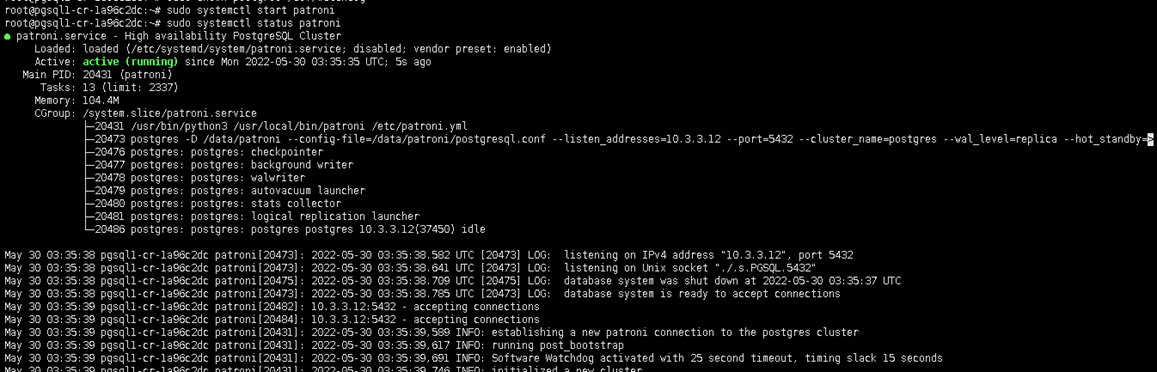
systemctl start patronisystemctl status patroni
pgsql1 as master.
We can see, the pgsql1 will act as the PostgreSQL master
pgsql2 and pgsql3 as slave
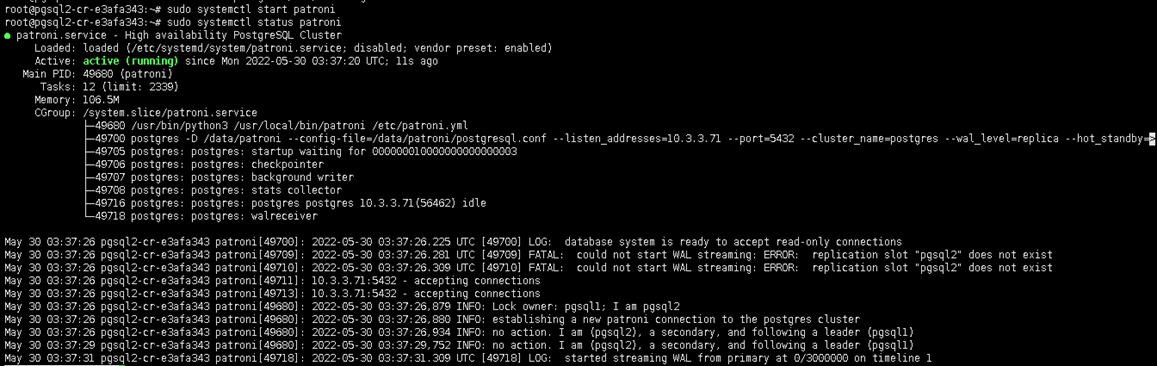
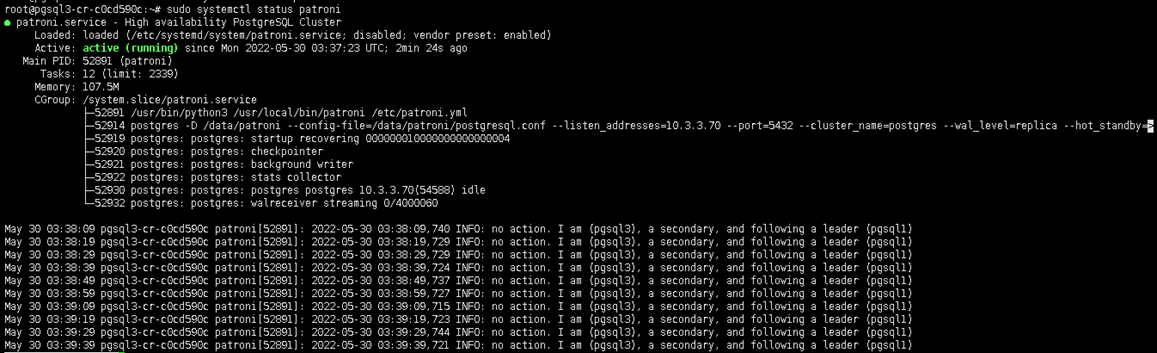
Install Haproxy
Our last step install HAproxy service to give us an endpoint to which the application can connect to the database.
sudo apt -y install haproxy
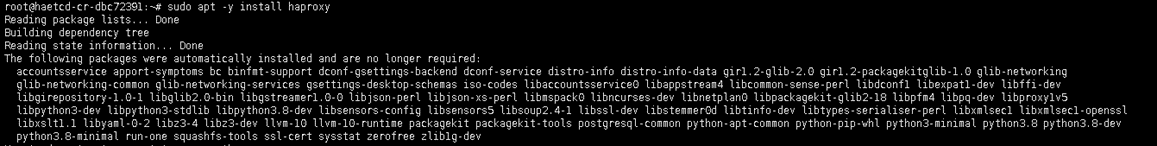
Edit the haproxy file configuration as follow
nano /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
global
maxconn 100
defaults
log global
mode tcp
retries 2
timeout client 30m
timeout connect 4s
timeout server 30m
timeout check 5s
listen stats
mode http
bind *:7000
stats enable
stats uri /
listen postgres
bind *:5000
option httpchk
http-check expect status 200
default-server inter 3s fall 3 rise 2 on-marked-down shutdown-sessions
server pgsql1 10.3.3.12:5432 maxconn 100 check port 8008
server pgsql2 10.3.3.71:5432 maxconn 100 check port 8008
server pgsql3 10.3.3.70:5432 maxconn 100 check port 8008
Check our haproxy configuration using the following command:
sudo /usr/sbin/haproxy -c -V -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg

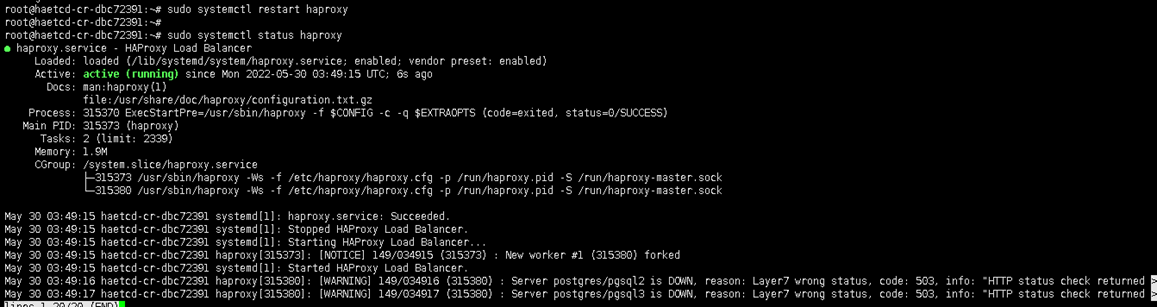
If the configuration is valid, we can restart our haproxy service
sudo systemctl restart haproxy
In the final step, we can monitor the PostgreSQL cluster using the browser as shown in the screenshot below:
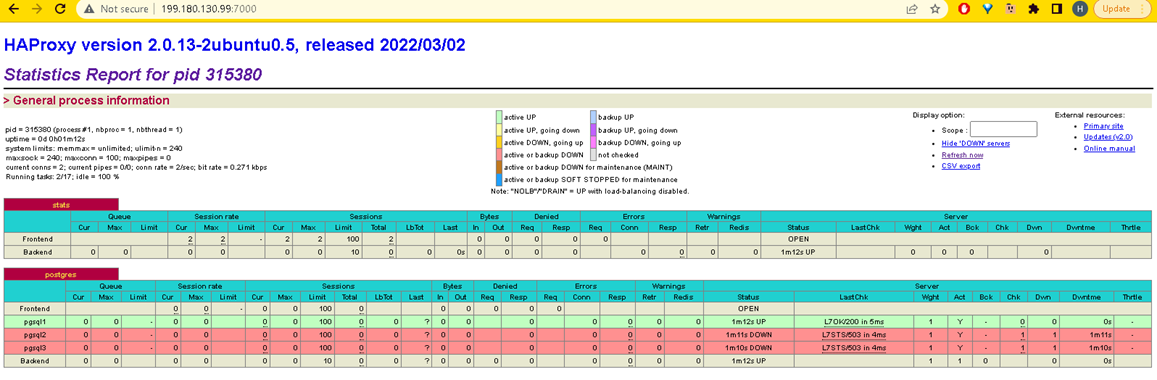
As we can see, psql1 is the leader of the PostgreSQL cluster with the green line row.
Now we will kill patroni service on psql1, to see which VM will be acting as the leader.
systemctl stop patroni
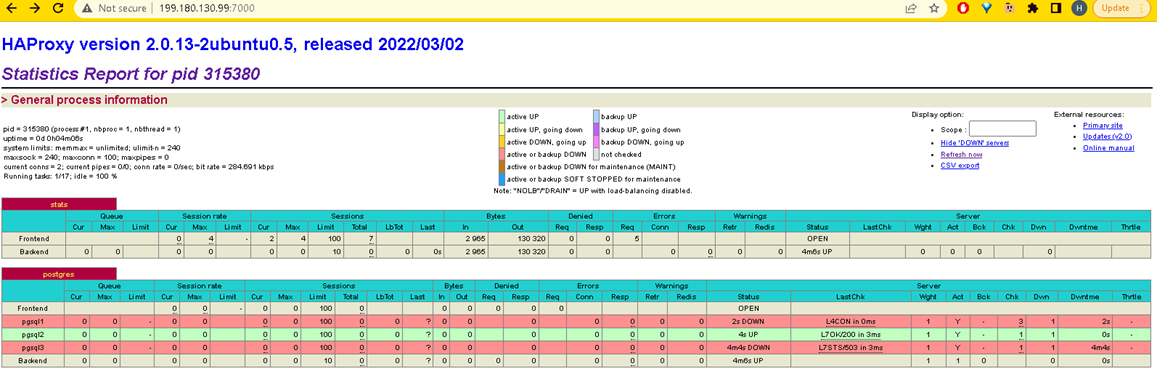
After we stop service patroni service in psql1, the psql2 will be elected as the leader node.
Test PostgresSQL Cluster
If we want to make a connection to PostgreSQL, we use the IP Address of HAProxy and port 5000.
su - postgres
psql -U postgres -h 199.180.130.99 -p 5000
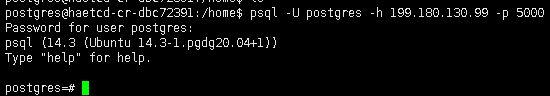
You now have a high availability PostgreSQL Cluster in Cloud Raya that is ready to use.
Please don’t hesitate to contact Cloud Raya support if you need further assistance.
Find more tutorials articles about Cloud Raya in our Knowledge Base, or if you want to get more general knowledge about technology feel free to visit our Blog.
Curious to know more about our products and panel? register here for free!.