-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
This tutorial will discuss the implementation of the Open AI Chat Model using PHP as the continuation of the previous tutorial where we talked about the Completions Model. Here, we will focus more on creating an interactive chatbot using Open AI API.
Before we go further, make sure you have read the previous tutorial because we will not discuss the basics, such as creating an OpenAI account or generating the API key, in this tutorial.
About Chats Models

Let’s recap about what and how Chats works. Chats is an assignment that allows users to directly interact with the model. The model will respond to every question or statement created by the user and answer it in sequence as if we are talking with a real human. This model is very useful to create a natural and dynamic conversation experience.
Model Selection and Its Distinction from Completions API
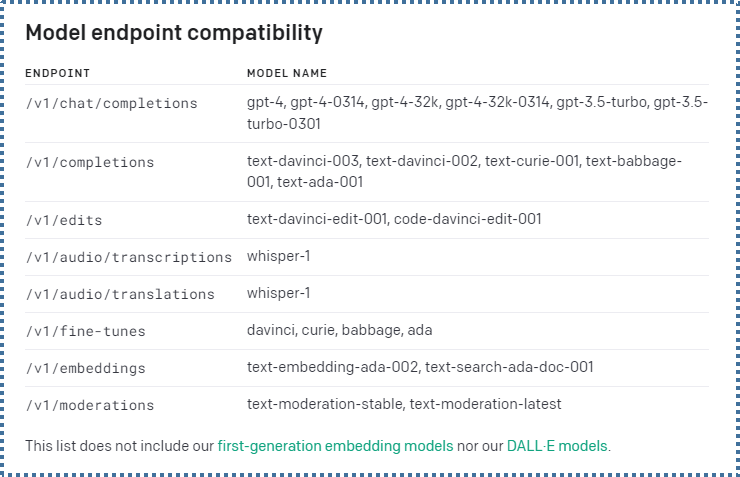
According to OpenAI documentation, the Chat Models use Endpoint https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions with gpt-3.5-turbo as the recommended standard model.
Meanwhile, the Completions Model uses Endpoint https://api.openai.com/v1/completions with text-davinci-003 as the recommended standard model.
The main difference between the Completions and Chats model is the ability to understand the context from previous interactions owned by Chats. Thus, Chats can generate more natural responses compared to the Completions model.
API Request Structure for Chats
The following is an example of API request structure for Chat models using cURL.
curl https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages": [
{"role": "system", "content": "Anda adalah asisten yang membantu dalam pertanyaan seputar destinasi wisata dengan penuh keramahan."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}
],
"temperature": 0.2,
"max_tokens": 512,
"top_p": 0.2,
"frequency_penalty": 0.0,
"presence_penalty": 0.6
}'
Now, we will convert it into a PHP
<?php
$openaiApiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY";
$data = array(
"model" => "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages" => array(
array("role" => "system", "content" => "Anda adalah asisten yang membantu dalam pertanyaan seputar destinasi wisata dengan penuh keramahan."),
array("role" => "user", "content" => "Hai!")
),
"temperature" => 0.2,
"max_tokens" => 512,
"top_p" => 0.2,
"frequency_penalty" => 0.0,
"presence_penalty" => 0.6
);
$curl = curl_init();
curl_setopt_array($curl, array(
CURLOPT_URL => "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions",
CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER => true,
CURLOPT_ENCODING => "",
CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS => 10,
CURLOPT_TIMEOUT => 30,
CURLOPT_HTTP_VERSION => CURL_HTTP_VERSION_1_1,
CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST => "POST",
CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS => json_encode($data),
CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER => array(
"Authorization: Bearer " . $openaiApiKey,
"Content-Type: application/json"
),
));
$response = curl_exec($curl);
$err = curl_error($curl);
curl_close($curl);
$result = json_decode($response, true);
$content = $result['choices'][0]['message']['content'];
echo $content;
?>The following is the result of the API request syntax seen from a browser.
Hai! Selamat datang di layanan bantuan destinasi wisata. Ada yang bisa saya bantu?
There are no significant changes in the essential and optional parameters, which you can configure directly in the API call. Like the model, temperature, max tokens, top probability, etc., like what we have learned from the previous tutorial.
However, in Chats API, we use the “messages” parameter instead of the “prompt” used by the Completions model. This parameter is also can be configured as an array.
Messages here refer to the question or statement given by the user, which requires two fields, role and content.
- role: message sender (
system,user, orassistant) - content: message content (such as, write me a beautiful poem)
These fields make the Chat model able to create more dynamic conversations.
Messages can also contain an optional field, called name. This field will give a name to the message sender, such as example-user, Alice, Blackbeadrbot, etc. The name cannot contain space.
The Chat model works by creating a conversation followed by clear instructions on what the model should do, followed by a message from the user, and lastly a message from the assistant.
Do note, that the gpt-3.5-turbo does not put heavy weight into the system message as if what gpt-4 does. Thus, it is recommended that all important instructions be placed in the message from users.
The Working of Chats
Let’s take a look at another example of the Chats API call to see how it works.
- In some cases, it is easier to show the model of what we want than tell the model of what we want.
One way to show the model of what we want is to create a false scenario:
<?php
$openaiApiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY";
$data = array(
"model" => "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages" => array(
array("role" => "system", "content" => "Kamu adalah asisten yang membantu dan mengikuti pola."),
array("role" => "user", "content" => "Bantu aku menerjemahkan contoh kiasan berikut"),
array("role" => "assistant", "content" => "Tentu, dengan senang hati!"),
array("role" => "user", "content" => "Hatinya lembut seperti?"),
array("role" => "assistant", "content" => "Kapas"),
array("role" => "user", "content" => "Pemikirannya keras seperti?"),
array("role" => "assistant", "content" => "Batu"),
array("role" => "user", "content" => "Tindakannya kasar seperti?")
),
"temperature" => 0.2,
"max_tokens" => 512,
"top_p" => 0.2,
"frequency_penalty" => 0.0,
"presence_penalty" => 0.6
);
$curl = curl_init();
curl_setopt_array($curl, array(
CURLOPT_URL => "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions",
CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER => true,
CURLOPT_ENCODING => "",
CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS => 10,
CURLOPT_TIMEOUT => 30,
CURLOPT_HTTP_VERSION => CURL_HTTP_VERSION_1_1,
CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST => "POST",
CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS => json_encode($data),
CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER => array(
"Authorization: Bearer " . $openaiApiKey,
"Content-Type: application/json"
),
));
$response = curl_exec($curl);
$err = curl_error($curl);
curl_close($curl);
$result = json_decode($response, true);
$content = $result['choices'][0]['message']['content'];
echo $content;
?>The following is the result of the API request syntax seen in browser.
Kerikil
- To tell the system that it is not a real conversation and should not be replicate for the second time by the model, we can change the name in the message from
systemtouser_exampleandassistant_example.
<?php
$openaiApiKey = "YOUR_API_KEY";
$data = array(
"model" => "gpt-3.5-turbo",
"messages" => array(
array("role" => "system", "content" => "Kamu adalah asisten yang membantu dan mengikuti pola."),
array("role" => "system", "name" => "user_contoh", "content" => "Bantu aku menerjemahkan contoh kiasan berikut"),
array("role" => "system", "name" => "assistant_contoh", "content" => "Tentu, dengan senang hati!"),
array("role" => "system", "name" => "user_contoh", "content" => "Hatinya lembut seperti?"),
array("role" => "system", "name" => "assistant_contoh", "content" => "Kapas"),
array("role" => "system", "name" => "user_contoh", "content" => "Pemikirannya keras seperti?"),
array("role" => "system", "name" => "assistant_contoh", "content" => "Batu"),
array("role" => "user", "content" => "Tindakannya kasar seperti?")
),
"temperature" => 0.2,
"max_tokens" => 512,
"top_p" => 0.2,
"frequency_penalty" => 0.0,
"presence_penalty" => 0.6
);
$curl = curl_init();
curl_setopt_array($curl, array(
CURLOPT_URL => "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions",
CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER => true,
CURLOPT_ENCODING => "",
CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS => 10,
CURLOPT_TIMEOUT => 30,
CURLOPT_HTTP_VERSION => CURL_HTTP_VERSION_1_1,
CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST => "POST",
CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS => json_encode($data),
CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER => array(
"Authorization: Bearer " . $openaiApiKey,
"Content-Type: application/json"
),
));
$response = curl_exec($curl);
$err = curl_error($curl);
curl_close($curl);
$result = json_decode($response, true);
$content = $result['choices'][0]['message']['content'];
echo $content;
?>The following is the result of the API request syntax seen in browser.
Kerikil
Further Improvisation
From the static script example above, we can make further improvements by adding an input field. The input field function as the receiver of the user message, which the model then generate the response to answer the message.
We can improve it further by developing the model to store the questions already asked by the user during the usage. This will create continuation in the discussion as asks things related to the previous questions.
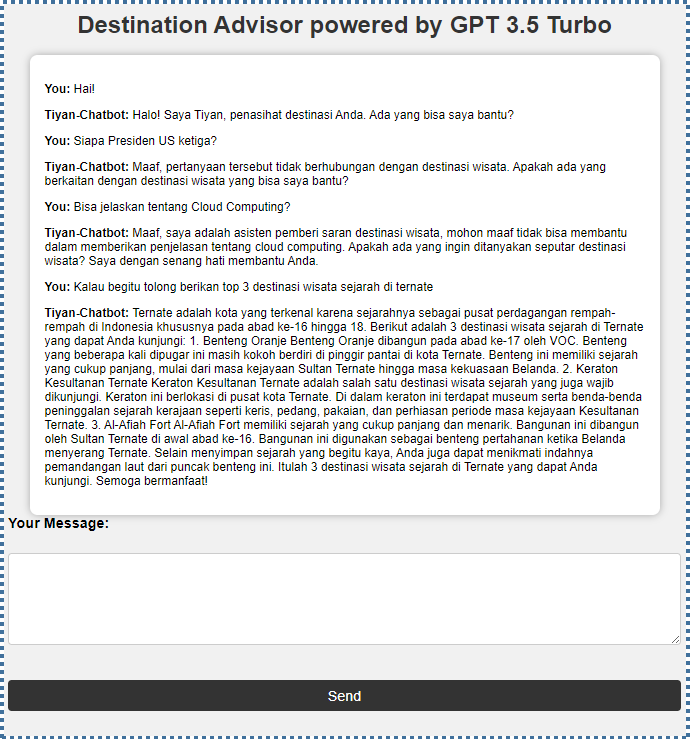
We have created a simple PHP application in CloudRaya’s VM as an example, which functions as a Trip Advisor that allows users to interact with the bot and ask about interesting tourism spots or deny the question if it does not relate to the tourism theme.
Conclusion
We hope this tutorial can help you understand on how to integrate OpenAI API for the Chat model in your website project using PHP language in CloudRaya’s VM.
Visit CloudRaya’s Knowledge Base for more tutorials surrounding cloud computing or you can visit our YouTube channel if you prefer a video format.