Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Easy Steps to Enable VPC in Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles ( 17 ) Collapse Articles
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles ( 53 ) Collapse Articles
- Articles coming soon
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles ( 25 ) Collapse Articles
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles ( 1 ) Collapse Articles
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles ( 3 ) Collapse Articles
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- Articles coming soon
Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
Introduction
Migrating your app’s platform to Kubernetes which has the capability to orchestrate the container management cycle, could fulfill the following needs of your organization.
Engaging The DevOps Culture
One of the needs to engage the DevOps culture is to encapsulate your apps and the dependencies needed into an image and then deploy the image into a container-based platform. That way each app will have its isolated environment and the deployment can be run automatically by adopting the CI/CD point of view.
Activate the CI/CD Deployment Cycle
Continuous integration in a practical way has meaning to building image and pushing it into private/public registries seamlessly.
Continuous Delivery means delivering the encapsulated image from available registries to a container platform. Kubernetes as a container orchestrator could create containers inside the Pod in a rather fancy way by investing the code from the manifest file.
To help the Dev and Ops team run the method seamlessly, we usually employ third-party tools such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, and many more.
Moving from Monolithic Apps to Microservices
Monolithic applications consist of components that are all tightly coupled together and must be developed, deployed, and managed as one entity because they all run as a single OS process.
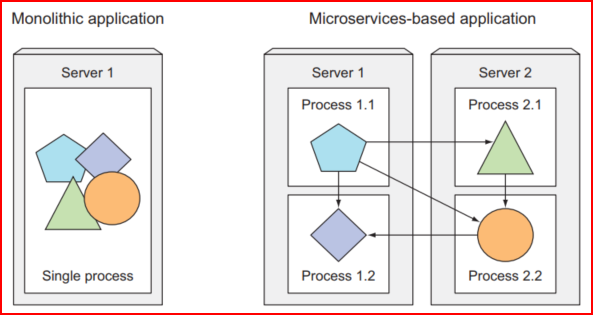
Splitting the big apps into a chunk of services has the advantage of scaling out and scaling up processes independently.
Unlike monolithic systems, where you need to scale the system as a whole, it is done on a per-service basis, which means you have the option of scaling only those services that require more resources while leaving others at their original scale.
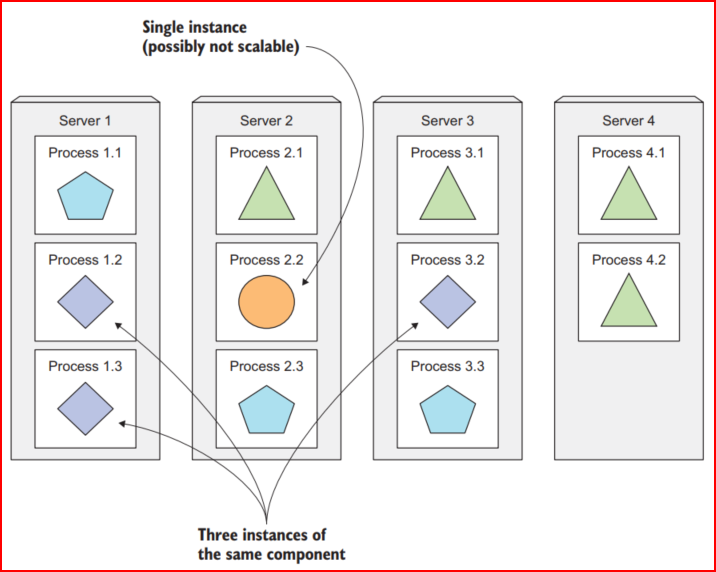
Providing a consistent environment for the apps
Kubernetes environment most likely stays the same across popular cloud platforms such as GKE, EKS, and AKS. That is because Kubernetes is a higher layer compared to the OS, and hardware adopted.
Thus, it makes Kubernetes stay consistent across multiple platforms.
In terms of an isolated environment, with Kubernetes, the application could have its own environment by differentiating them in the namespace layer, deployment layer, or pod layer.
K8S Provisioning with RKE
The explanation of how to create the K8s cluster using RKE can be obtained in the following article:
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
Another add-on explanation around RKE in Cloud Raya:
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in Cloud Raya
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
Study Case
Replatforming e-commerce Laravel Bagisto project with composer
The installation guide for the Bagisto project could be attained in the following URL,
The official documentation for the Bagisto project installation is within the virtual machine environment. Therefore, the replatforming procedure may need to follow the following steps.
- Write the Dockerfile for image building.
- Write the manifest files for K8s deployment.
- Activate the CI/CD procedure using GitLab CI.
Image Build Stage
PHP environment sets:
- PHP Version 8.0.x
- MySQL 8.0.x
- PHP Module (outside the default modules): pdo pdo_mysql bcmath gd exif zip mysqli intl
Downloading Bagisto
composer create-project bagisto/bagistoSetting the .env Variables
Key takeaway for .env variables configuration
Also don’t forget to remove .env from .gitignore file
APP_URL
DB_CONNECTION
DB_HOST
DB_PORT
DB_DATABASE
DB_USERNAME
DB_PASSWORDexample the .env generated from composer create project
APP_NAME=Bagisto
APP_ENV=local
APP_VERSION=1.4.3
APP_KEY=
APP_DEBUG=true
APP_URL=https://APP_URL
APP_ADMIN_URL=admin
APP_TIMEZONE=Asia/Kolkata
APP_LOCALE=en
APP_CURRENCY=USD
LOG_CHANNEL=stack
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=Enter your DB Host // Enter your DB cluster service name
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=Enter your DB Name
DB_USERNAME=Enter your DB User
DB_PASSWORD=Enter your DB password
#DB_PREFIX=
BROADCAST_DRIVER=log
CACHE_DRIVER=file
SESSION_DRIVER=file
SESSION_LIFETIME=120
QUEUE_DRIVER=sync
REDIS_HOST=Enter your Redis cluster service name
REDIS_PASSWORD=null
REDIS_PORT=6379
MAIL_DRIVER=smtp
MAIL_HOST=smtp.mailtrap.io
MAIL_PORT=2525
MAIL_USERNAME=
MAIL_PASSWORD=
MAIL_ENCRYPTION=tls
SHOP_MAIL_FROM=
ADMIN_MAIL_TO=
MAIL_FROM_NAME=
FIXER_API_KEY=
EXCHANGE_RATES_API_KEY=
PUSHER_APP_ID=
PUSHER_APP_KEY=
PUSHER_APP_SECRET=
PUSHER_APP_CLUSTER=mt1
MIX_PUSHER_APP_KEY="${PUSHER_APP_KEY}"
MIX_PUSHER_APP_CLUSTER="${PUSHER_APP_CLUSTER}"
FACEBOOK_CLIENT_ID=
FACEBOOK_CLIENT_SECRET=
FACEBOOK_CALLBACK_URL=https://yourhost.com/customer/social-login/facebook/callback
TWITTER_CLIENT_ID=
TWITTER_CLIENT_SECRET=
TWITTER_CALLBACK_URL=https://yourhost.com/customer/social-login/twitter/callback
GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID=
GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET=
GOOGLE_CALLBACK_URL=https://yourhost.com/customer/social-login/google/callback
LINKEDIN_CLIENT_ID=
LINKEDIN_CLIENT_SECRET=
LINKEDIN_CALLBACK_URL=https://yourhost.com/customer/social-login/linkedin/callback
GITHUB_CLIENT_ID=
GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET=
GITHUB_CALLBACK_URL=https://yourhost.com/customer/social-login/github/callback
Write the Dockerfile
Dockerfile is the essential element to build our image and push it to either the private or public registry.
The code below is an example of Dockerfile image build for Bagisto e-commerce project.
FROM php:8.0-fpm-alpine
# Init preparation
RUN apk update && apk upgrade \
&& apk add libzip-dev libpng-dev inetutils-telnet vim icu-dev \
&& docker-php-ext-install pdo pdo_mysql bcmath gd exif zip mysqli intl
#
# Activate PHP Prod variable
RUN cp "$PHP_INI_DIR/php.ini-production" "$PHP_INI_DIR/php.ini"
# Data migration and preparation
WORKDIR /usr/local/bin
RUN wget https://getcomposer.org/download/2.5.5/composer.phar
RUN mv composer.phar composer && chmod +x composer
RUN mkdir -pv /var/www/html/web-data # Will be used as apps root directory
RUN mkdir -pv /apps
# Copy the local bagisto project to the image directory
COPY bagisto/ /apps/
RUN chown -R 777 /apps/storage/
WORKDIR /apps
RUN echo yes | composer install
RUN php artisan storage:link
RUN php artisan key:generate
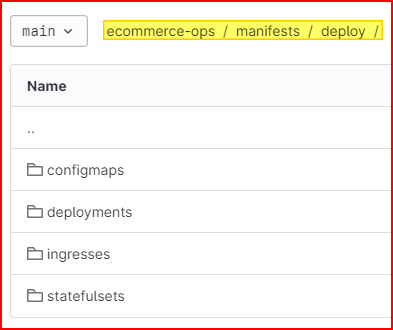
Write Manifest files for K8s deployment
The example of the manifest files directory structure for the K8s deployment
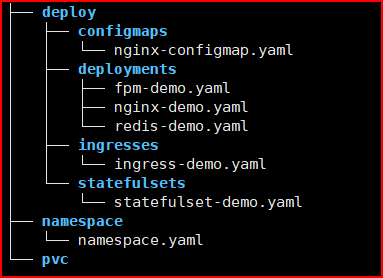
Please refer to the repository below to see the full source code of the K8s manifest files.
>> e-commerce open source – GitLab
- Screenshot snippets
Activate The CI/CD Procedures with GitLab CI
CI/CD is the key to automate the image build process and the manifest deployment to the K8s cluster.
Using a tool such as GitLab CI, the CI/CD development procedure can be attainable in a proper way.
First, you need to create the .gitlab-ci.yml on the current branch of your repository.
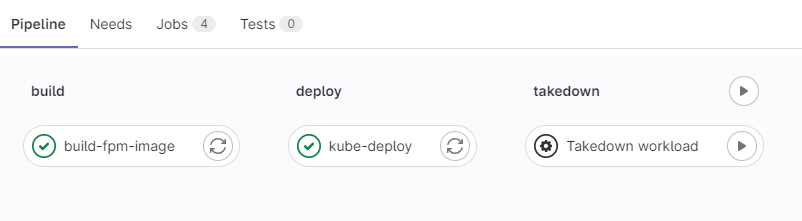
The content of the GitLab CI should consist of the following stages:
- Build stage: The stage of continuous integration image build and push to the registry
- Deploy stage: The stage of continuous deployment manifest files to the K8s cluster
- Takedown stage: Optional stage to delete all resources in the related namespace
Source Code Snippet on .gitlab-ci.yml
Image Build Stage
## Example of the required variables
variables:
IMAGE_TAG1: "v4"
KUBE_AGENT_PATH: "ahmadnromiz/kube-agent"
IMAGE_FPM: "index.docker.io/sultanahmad/fpm-hospital:$IMAGE_TAG1"
FPM_PATH: "image-build/fpm/Dockerfile"
FPM_CONTEXT_DIR: "dir://image-build/fpm"
CI_REGISTRY: "index.docker.io"
## Stages
stages:
- build
- deploy
- takedown
## Image Build Stage
build-fpm-image:
image:
name: gcr.io/kaniko-project/executor:debug
entrypoint: [""]
stage: build
cache:
key: "modules-cache"
paths:
- /apps/node_modules/
- /apps/vendor/
variables:
APP_URL: (fill with the URL of your apps, e.g. bagisto.example.com)
DB_USER: root
DB_HOSTNAME: (fill with the database cluster IP service)
REDIS_HOSTNAME: (fill with the redis cluster IP service)
NAME_REDIS: (redis deployment name)
DB_NAME: (database name)
before_script:
- sh image-build/script.sh # pre-build script to replace some strings
# Script job to build image and push it to the registry
script:
- echo "{\"auths\":{\"$CI_REGISTRY\":{\"username\":\"$CI_REGISTRY_USER\",\"password\":\"CI_REGISTRY_PASSWORD\"}}}" > /kaniko/.docker/config.json
- /kaniko/executor
--context=$FPM_CONTEXT_DIR
--dockerfile=$FPM_PATH
--destination "${IMAGE_FPM}"
tags:
- mamad
# Workflow Rules
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TITLE =~ /^redeploy/
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TITLE =~ /^build image/
The Manifest Deploy Stage and The Takedown Stage (optional)
# Kube Prepare
.kube_prepare:
image:
name: bitnami/kubectl:1.26.1
entrypoint: ['']
before_script:
- ./pre_deploy.sh
- mkdir -pv ssl/
- cat "$FULLCHAIN" > ssl/fullchain.pem && cat "$PRIVKEY" > ssl/privkey.pem
- kubectl config get-contexts
- kubectl config use-context ${KUBE_AGENT_PATH}:${KUBE_AGENT_NAME}
- kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=${KUBE_NAMESPACE}
script:
- ./script_deploy.sh
#Deploy to RKE cluster
kube-deploy:
stage: deploy
variables:
KUBE_ACTION: apply
KUBE_ACTION2: delete
MANIFEST_PATH: manifests
NAMESPACE: $KUBE_NAMESPACE
APP_URL: bagisto.ahmadcloud.my.id
CERT_NAME: star.ahmadcloud.my.id
DB_USER: user_db
DB_NAME: bagisto
NAME_FPM: project-app
NAME_NGINX: nginx-app
NAME_REDIS: redis-app
NAME_CONFIGMAP: bagisto-cfm
NAME_INGRESS: bagisto-ingress
tags:
- mamad
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TITLE =~ /^redeploy/
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TITLE =~ /^rancher deploy/
extends: .kube_prepare
## Takedown Stage (optional)
"Takedown workload":
stage: takedown
when: manual
variables:
NAMESPACE: $KUBE_NAMESPACE
TAKEDOWN: activate
KUBE_ACTION: delete
MANIFEST_PATH: manifests
extends: .kube_prepare
tags:
- mamad
rules:
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TITLE =~ /^redeploy/
- if: $CI_COMMIT_TITLE =~ /^rancher deploy/
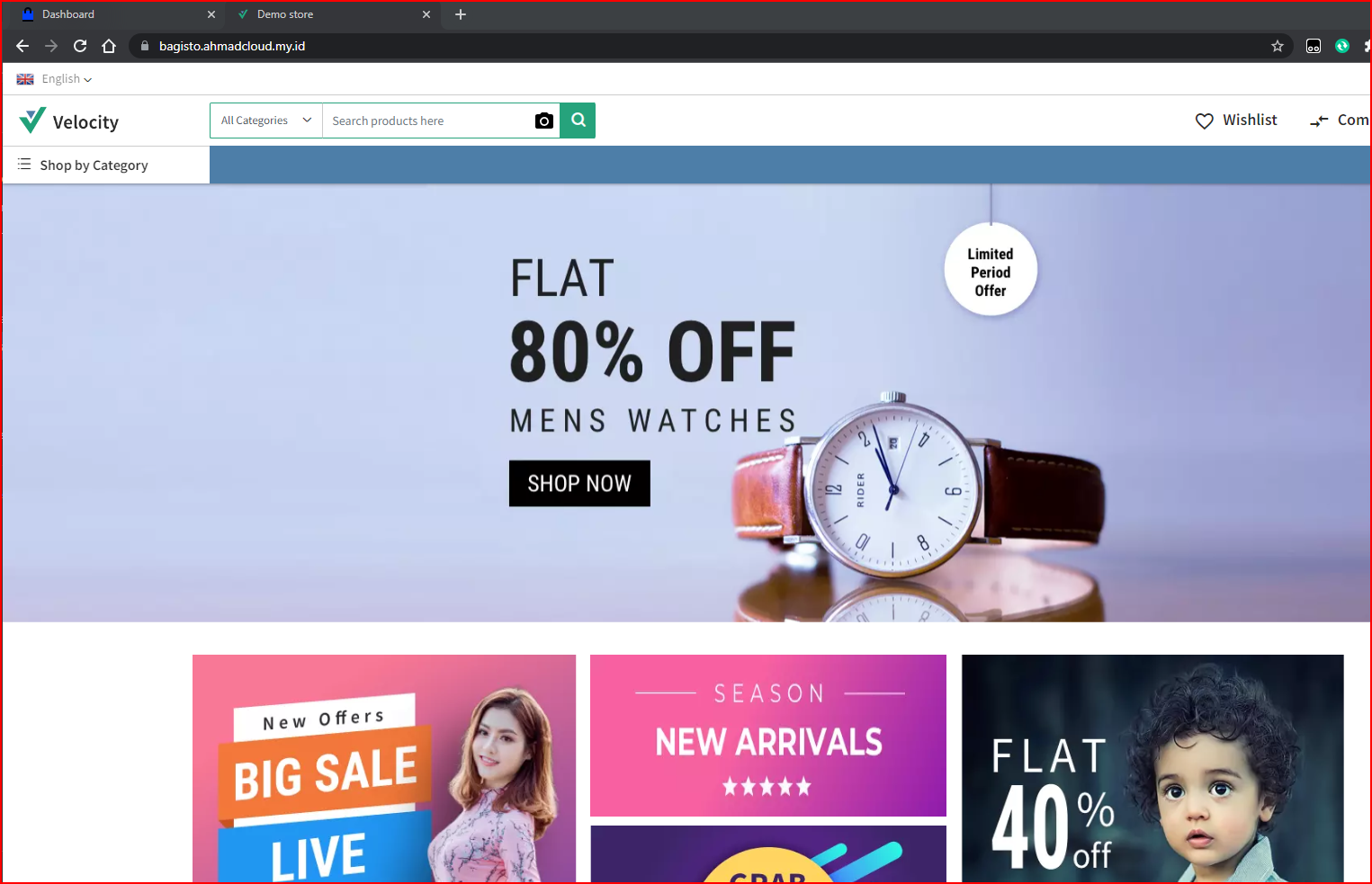
Apps Screenshots
Homepage Demo Store
Admin Page Dashboard
Pipeline screenshot
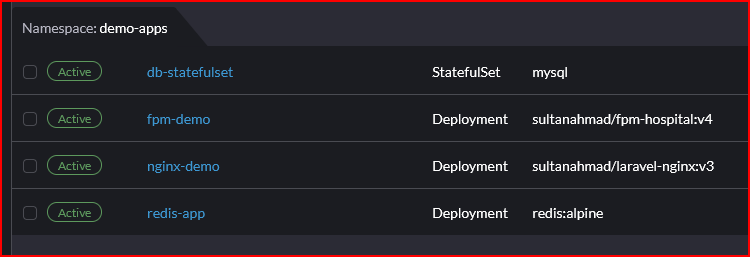
Rancher Workloads and Related Resources
- Workloads
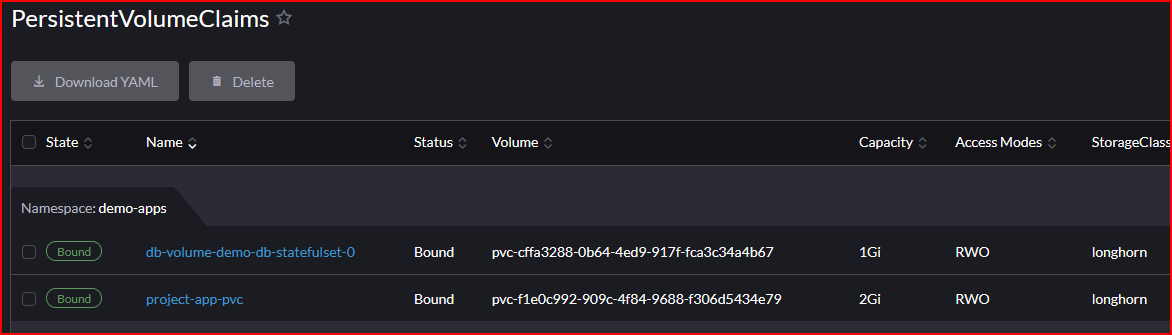
- Persistent Volume Claims provisioned with Longhorn
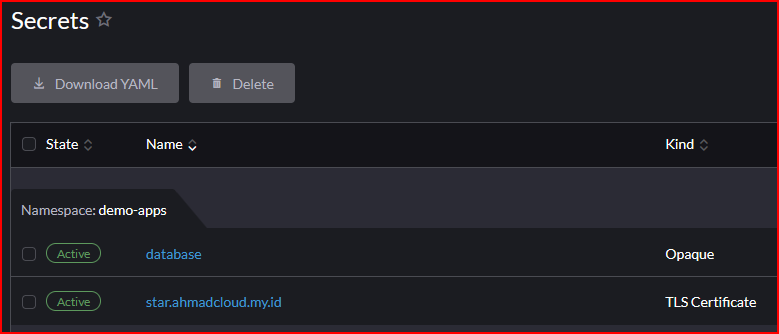
- Secrets
- Services
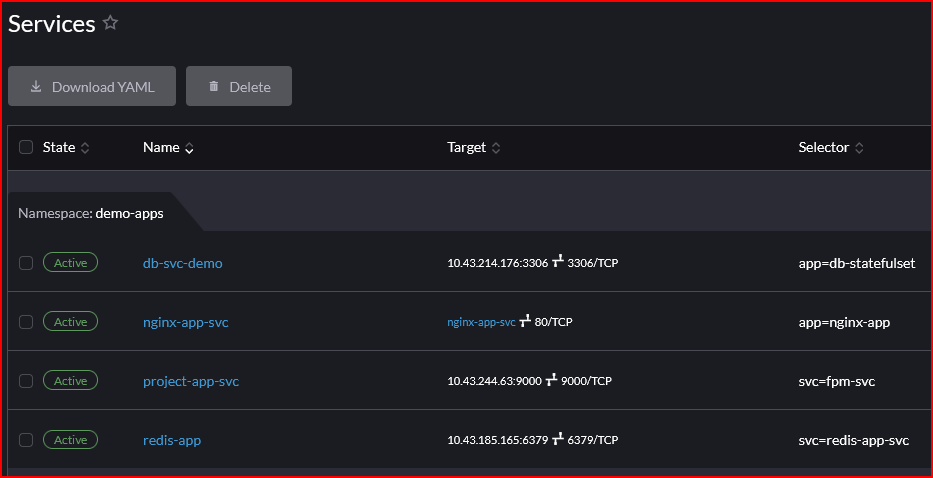
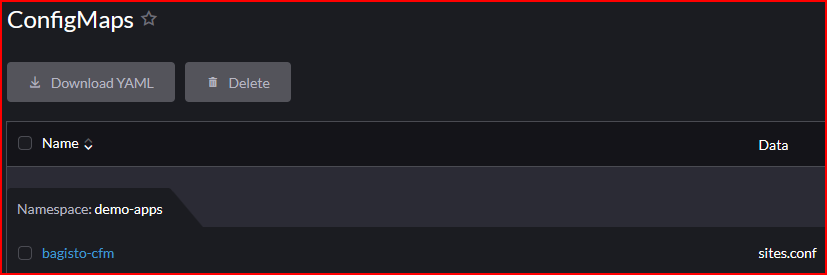
- Config Maps
Conclusion
Developing apps in the containerized infrastructure has significant benefits based on the explanation above.
We are approaching the implementation of DevOps culture as we transition our applications from a virtual machine-based infrastructure to a container-based one.
Adopting the CI/CD approach on a K8s cluster simplifies the development process by automating it. GitLab CI is a tool that facilitates the creation of a seamless CI/CD process.
Please give your ratings or comment, let me know about your thoughts, and have a discussion. Check more tutorials on our knowledge base or video stream them on our youtube channel.