-
Products and Features
- Getting Started with CloudRaya Container Registry
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Generating a CloudRaya API key
- Simplify CloudRaya Management with API
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on KubeRaya
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Opening Ping Access on Cloud Raya VM Public IP
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- How to Create Project Tag in Cloud Raya for More Organized VM Billing Report
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- SSO Management on Cloud Raya
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Cloud Raya Load Balancer, Solution to Distribute Load Equally
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- Fix Broken LetsEncrypt SSL Certificate due to Expired Root CA Certificate
- How to Make a Snapshot and Configure VM Backup in Cloud Raya
- How to Request Services or Licenses Products
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Managing your DNS Zone with DNS Bucket in Cloud Raya
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Load Balancing in Cloud Raya
- Establishing a VPN in Cloud Raya
- Generating an API Token
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
- Show Remaining Articles16 Collapse Articles
-
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
-
- Maximizing StorageRaya with Essential Practices
- Using StorageRaya – CloudRaya S3 Object Storage
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Maximize Your Storage Raya Access Speed with Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Assign Multiple IP Addresses to Virtual Machine
- Deploying a Virtual Machine on CloudRaya
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Exporting Cloud Raya VM to outer Cloud Raya's Infrastructure using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Adding, Attaching, and Resize Root Storage Disk in Cloud Raya VPS
- Create VM, Custom Package, Reinstall VM, and Adjusting Security Profile
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Backing-Up Cloud Raya Windows VM Using Acronis Cyber Protect
- Deploying a Virtual Machine in Cloud Raya
-
Integration
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Replatforming Apps to K8s with RKE and GitLab CI
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- How to Install Podman on Almalinux/Rocky Linux 9
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up High Availability PostgreSQL Cluster Using Patroni on Cloud Raya
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Kubernetes Ingress Controller using SSL in CloudRaya
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to install and secure MariaDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04 on Cloud Raya
- How to Install and Securing MongoDB on Ubuntu 18.04 and 20.04
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles53 Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Improving Email Delivery with Sendinblue SMTP Relay
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- ElkarBackup: GUI Based backup Tools based on Rsync and Rsnapshot
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Upgrade Zimbra and the OS Version
- Deploy Mailu on Rancher Kubernetes
- Managing Storage Raya from various tools and from various OS
- Binding NextCloud with CloudRaya S3 Object Storage as External Storage Mount
- Simple monitoring and alerting with Monit on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- VS Code on your browser! How to install code-server on a VM
- Implementing Redis HA and Auto-Failover on Cloud Raya
- Using XFCE Desktop Environment on Cloud Raya VM
- Implementing Continuous Integration with Gitlab CI and Continuous Delivery with Rancher Fleet
- Using Collabora Online on Cloud Raya NextCloud's VM
- Installing NextCloud in Cloud Raya- Detail Steps from the Beginning to the Very End
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Monitor Your Services Uptime Using Uptime Kuma
- Create your own VPN server with DNS-Level AdBlocker using PiVPN
- How to deploy Portainer on Linux to easily manage your docker containers
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 3
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 2
- High Availability Kubernetes Using RKE in Cloud Raya Part 1
- How to Install Nextcloud on Cloud Raya
- Classes: Post Installation on Ansible
- Classes: Install and Configure Ansible
- Classes: Introduction to Ansible for a robust Configuration Management
- Connect Windows Active Directory on Cloud Raya with Azure AD
- How to Host Your Own Docker Hub in Cloud Raya
- How to Deploy Container in Cloud Raya using Docker
- Show Remaining Articles25 Collapse Articles
-
- Accessing KubeRaya Cluster Using the Kubernetes Dashboard
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Automating Task with Cronjob
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- How to Install Node.js and Launch Your First Node App
- How to Setup Your Own Laravel with Nginx in Ubuntu 18.04
- Install a Node.js and Launch a Node App on Ubuntu 18.04
-
- How to use Sudo on a CloudRaya Linux VM
- Keeping Your CloudRaya Linux VMs Up-to-Date
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication on CloudRaya Linux VM
- Using SSH Key on CloudRaya VM with PuTTY
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Export and Import Database in MySQL or MariaDB Using Mysqldump
- Backup & Sync Local and Remote Directories Using RSYNC
- How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 2
- Set Up WAF KEMP in Cloud Raya Part 1
- Using the SSH key Feature in Cloud Raya Dashboard
- How to backup Linux VM via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- How to Backup Desktop Linux and Windows via Acronis in Cloud Raya
- Securing CentOS with iptables
- Securing Ubuntu with UFW
- Show Remaining Articles1 Collapse Articles
-
- Configurating cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya – Part 2
- Deploying cPanel Using Ubuntu 20.04 on CloudRaya - Part 1
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- Building an Email Server on CloudRaya Using iRedMail
- Building a Self Hosted Password Manager Using Passbolt
- Improving Webserver Performance with SSL Termination on NGINX Load Balancer
- Using NGINX as an HTTP Load Balancer
- Installing Python 3.7-3.9 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy LTS using PPA
- Reverse Proxy management using Nginx Proxy Manager
- Install and Configure Squid Proxy in Ubuntu
- Installing Apache and Tomcat: A Quick Way
- Installing LAMP in Ubuntu
- Installing LEMP Stack on Ubuntu 18.04
- Show Remaining Articles3 Collapse Articles
-
- Building a Static Website Using Storage Raya S3 Bucket
- Integrating S3 Storage Raya and Strapi for Asset Storage Optimization – Part 4
- Integrating Strapi Content to Frontend React - Part 3
- Content Management with Strapi Headless CMS - Part 2
- Strapi Headless CMS Installation in CloudRaya - Part. 1
- Creating Interactive Chatbot with OpenAI API in PHP
- Installing Multiple PHP Versions in One VM for More Flexible Web Development
- OpenAI API Integration: Completions in PHP
- Hosting Static Website with Hugo on Cloud Raya
- Deploying Magento on Cloud Raya
- How to Install CWP in Cloud Raya
- How to Setup Active Directory Domain Service & DNS with Cloud Raya
-
- Articles coming soon
How to Deploy Django App on Cloud Raya VM Using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx
A basic guide on how to deploy Django app, using Gunicorn, Supervisor, and Nginx stack on your Cloud Raya VM instance.
In this article, I will be using Ubuntu 22.04 LTS as the deployment server, Python 3.8 and Django 4.0.
TLDR
- Create a standard user called apps
- Install supervisor and nginx
sudo apt install supervisor nginx -y- Install your App’s Python version.
- Install
pip - Install
pipenvglobally.
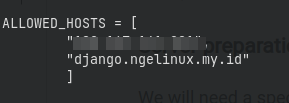
sudo pip install pipenv- Add your server IP and/or FQDN address to ALLOWED_HOSTS in
settings.pyfile
ALLOWED_HOSTS = [ "xx.yy.dd.zz", "your.domain.tld" ]- Copy the django app to
/home/apps/django-app - Go to the app folder and run:
cd /home/apps/django-app
python3.8 -m pipenv install --deploy- Install Gunicorn using pipenv on the same directory
python3.8 -m pipenv install gunicorn- Create supervisor config file under
/etc/supervisor/conf.d/django-app.conf
[program:django-app]
user=apps
directory=/home/apps/django-app/djangoapp/
command=/usr/local/bin/pipenv run gunicorn --workers=3 djangoapp.wsgi
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stdout_logfile=/home/apps/logs/django-app.log
stderr_logfile=/home/apps/logs/django-app.err.log- Create the required files and folder:
mkdir /home/apps/logs/
touch /home/apps/django-app{,.err}.log- Restart supervisor to recognize the app
sudo systemctl restart supervisor- Create nginx server block file for the app under
/etc/nginx/sites-available/django-app.conf
server {
listen 80;
location / {
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
}
}- Activate the config and reload nginx
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/django-app.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
sudo unlink /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
sudo nginx -t
sudo nginx -s reload- Access the app from your browser:
http://your-iporhttp://your-domain.tldand DONE!
Step-by-step Guide
Django App Peparation
I will assume that your Django App is ready to be deployed. This means it has Pipfile or requirements.txt. For this tutorial, I’m going to use pipenv as the virtual environment tool and here’s the directory structure of the app:
├── djangoapp
│ ├── db.sqlite3
│ ├── djangoapp
│ │ ├── asgi.py
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── settings.py
│ │ ├── urls.py
│ │ └── wsgi.py
│ └── manage.py
├── Pipfile
└── Pipfile.lockMake sure the app runs successfully in our local environment by running the below command on the app directory:
pipenv run djangoapp/manage.py runserver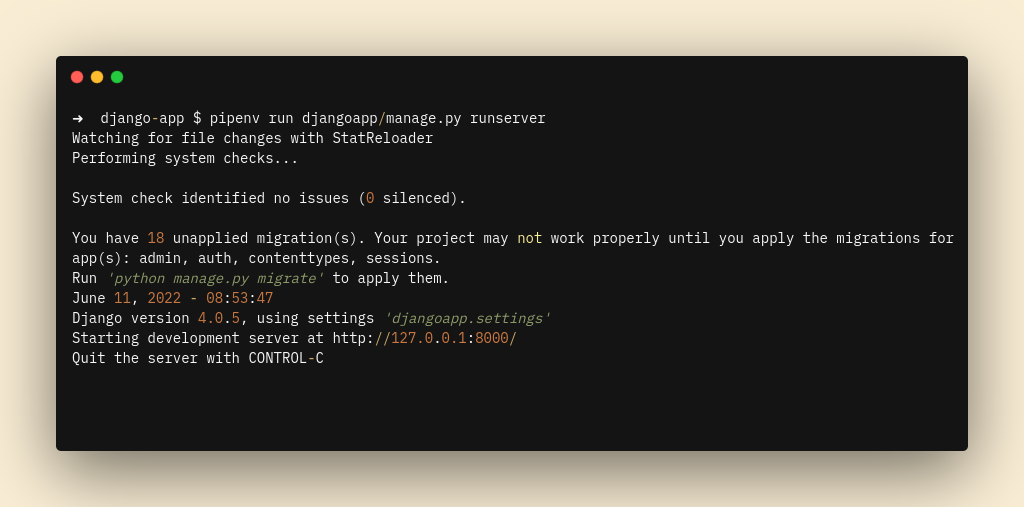
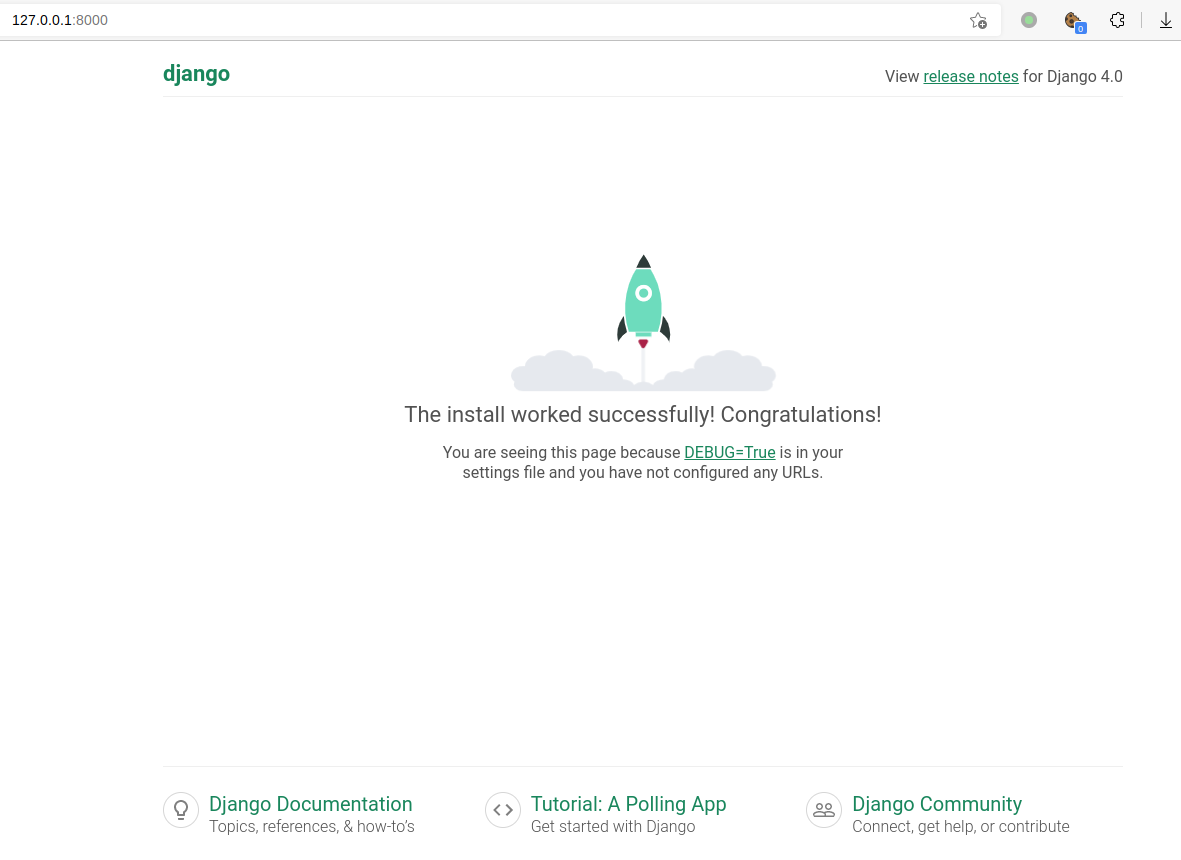
Then access your browser with http://127.0.0.1:8000
Add your server IP and/or domain to ALLOWED_HOST entry in the settings.py file, then save it.
Good, now we are ready to do the deployment.
Server Preparation
We will need a specific user that we will use to serve the app, and it should be a non administrative user. To simplify, we will create apps user
sudo useradd --create-home --shell /bin/bash appsWe will also want to install supervisor and nginx from now
sudo apt update && sudo apt install supervisor nginxAs mentioned earlier, we will be using Python 3.8 which isn’t available by default, so please take a look at this article on how to install Python 3.8 on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy. Don’t forget to install pip as well.
Then install pipenv globally:
sudo pip install pipenv
Copy App Files
Copy or clone (using git if it’s supported) the app files to /home/apps/django-app. You can use FTP, SFTP, SCP or any other means of transferring local files to the remote server. On the remote server, the apps directory should look like follows:
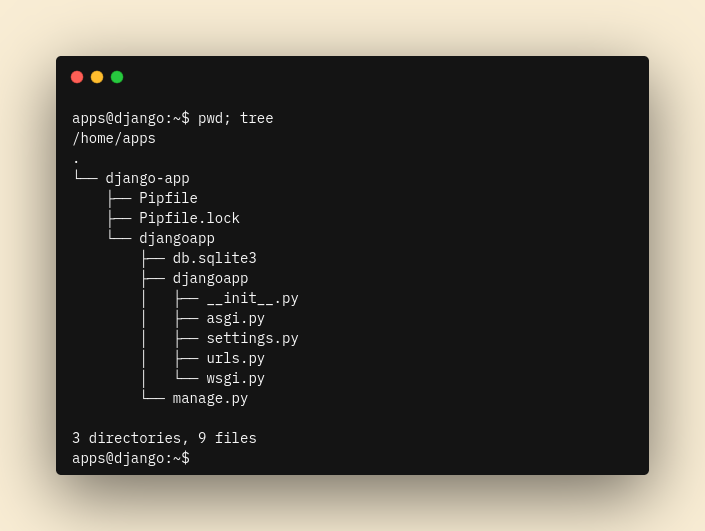
Install Required Dependencies
A good thing about pipenv is that it will automatically creates a virtual environment upon installing any required dependencies listed in the Pipfile. So, on the django-app folder run:
# make sure it's on /home/apps/django-app
python3.8 -m pipenv install --deploy
Next, we will install gunicorn:
python3.8 -m pipenv install gunicornThen, we will try to serve the app using gunicorn to test, but make sure you run the gunicorn from the app folder where manage.py resides:
cd djangoapp/
python3.8 -m pipenv run gunicorn djangoapp.wsgiIt should return something like this:
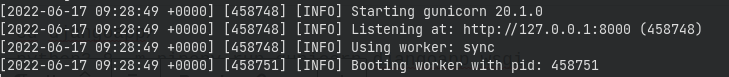
Awesome. Now we can setup supervisor to handle gunicorn process(es).
Install and Configure Supervisor
For Debian-based distros, run:
sudo apt install supervisorFor RHEL-based distros, run:
sudo dnf install supervisor
# or
sudo yum install supervisorThen, we will create a config file for the django app in /etc/supervisor/conf.d/ and name it as django-app.conf. Write or just copy the following lines to the file:
[program:django-app]
user=apps
directory=/home/apps/django-app/djangoapp
command=/usr/local/bin/pipenv run gunicorn --workers=3 djangoapp.wsgi
autostart=true
autorestart=true
stdout_logfile=/home/apps/logs/django-app.log
stderr_logfile=/home/apps/logs/django-app.err.logDon’t forget to create the ./logs/ folder to store the app’s logs:
# as the apps user
mkdir /home/apps/logsThen restart supervisor:
sudo systemctl restart supervisorMake sure it’s running by checking supervisor status:
sudo systemctl status supervisor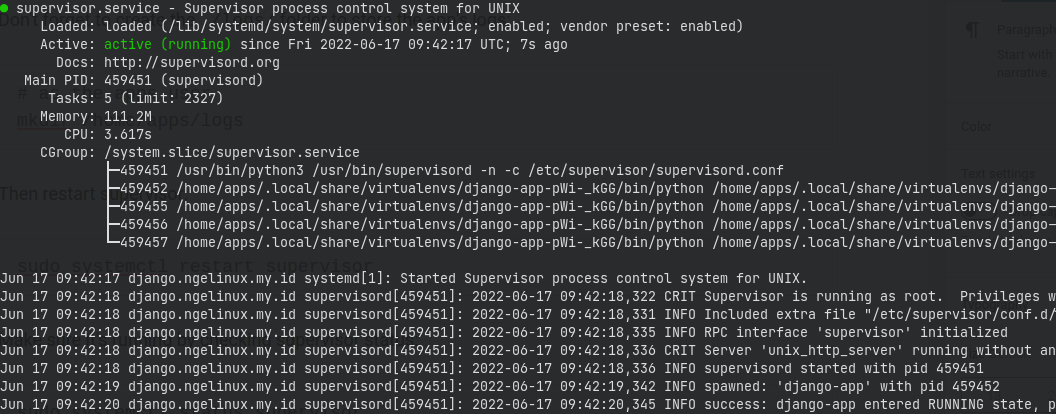
Next, we will install Nginx and configure it so it proxies the connection.
Install and Configure NGINX
Here, nginx will proxy HTTP connections to the gunicorn workers. This will also make SSL setup easier, but I won’t explain it here. Install nginx and make sure it’s started on boot:
sudo apt install nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx --nowThen create a new config file in /etc/nginx/sites-available for Ubuntu-based distros, RHEL-based ones should be in /etc/nginx/conf.d
server {
listen 80;
location / {
include proxy_params;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
}
}Save it as django-app.conf. Then for Ubuntu-based distro only, create a symlink in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ for the config file:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/django-app.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/django-app.confRemove the default site config
sudo unlink /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultFor RHEL-based distros, one might need to remove the default config or just rename the extension to .bak or something else. Then, test nginx and reload it
sudo nginx -t
sudo nginx -s reloadAccess Test
Finally, test it from your browser via http://YOUR-IP or http://YOUR-DOMAIN.TLD
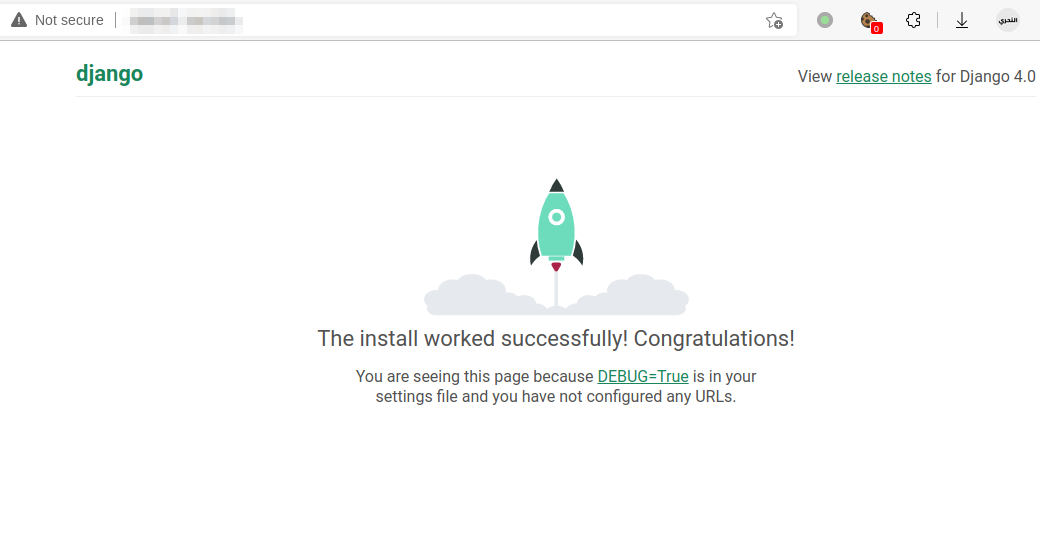
Yay! You’re now able to deploy your django app!
IMPORTANT NOTE: This is a basic setup which is insecure. A complete documentation on how to configure your django so it fits production deployment, please refer to this official documentation
Conclusion
We just learned how to deploy a django application using Pipenv as the virtual environment tool, Gunicorn as the Web Server Gateway, Supervisor as the process manager and finally, NGINX as the reverse proxy.
Find more tutorial articles in Cloud Raya’s Knowledge Base, or if you need article with more general topics about technology, feel free to visit our Blog. Even better, register now for free in Cloud Raya’s panel to try our overall products.